
Introduction
The process of screening participants for clinical trials is crucial to ensure eligibility based on study-specific criteria. Traditionally, this has been a manual task, requiring significant resources and time, which often leads to high costs and lengthy trial durations. However, advancements in natural language processing (NLP), particularly with large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, offer promising solutions. This article explores the RECTIFIER framework, which leverages GPT-4 to improve the accuracy and efficiency of clinical trial screening.
The Challenge of Traditional Screening Methods
Screening potential participants for clinical trials has traditionally relied on the diligence and judgement of study staff and healthcare professionals. This manual approach, while thorough, is prone to human error and requires substantial resources and time. For instance, the cost per screened patient for a phase 3 trial using traditional methods is approximately $34.75. Given these challenges, there is a growing need for more efficient and cost-effective screening methods.
The Promise of NLP and LLMs in Clinical Trials
Natural language processing (NLP) has shown potential in automating the extraction and analysis of relevant data from electronic health records (EHRs) and other sources. Traditional NLP methods, including rule-based systems and advanced semantic processing, have limitations, particularly in handling complex, unstructured data commonly found in EHRs. However, large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 have significantly advanced the state-of-the-art performance in many NLP tasks. Notably, LLMs have shown promise in medical applications, including diagnostics and trial matching.
Introducing the RECTIFIER Framework
The RECTIFIER (RAG-Enabled Clinical Trial Infrastructure for Inclusion Exclusion Review) framework leverages GPT-4 within a specialised Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architecture. This system is designed to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of clinical trial screening, particularly in scenarios where unstructured data are prevalent, and structured data may be incomplete or inaccurate.
Performance and Cost Efficiency
In a study, RECTIFIER demonstrated high accuracy in screening patients for clinical trials when tested in the Co-Operative Program for Implementation of Optimal Therapy in Heart Failure (COPILOT-HF). This study was designed to investigate the comparative effectiveness of two remote-care strategies to optimise guideline-directed medical therapy in patients with heart failure. During this actively enrolling heart failure clinical trial, RECTIFIER’s performance surpassed traditional methods. The cost of using RECTIFIER was only 11 cents per patient, a significant reduction compared to traditional screening methods. These findings suggest that RECTIFIER can substantially improve the efficiency of patient recruitment for clinical trials.
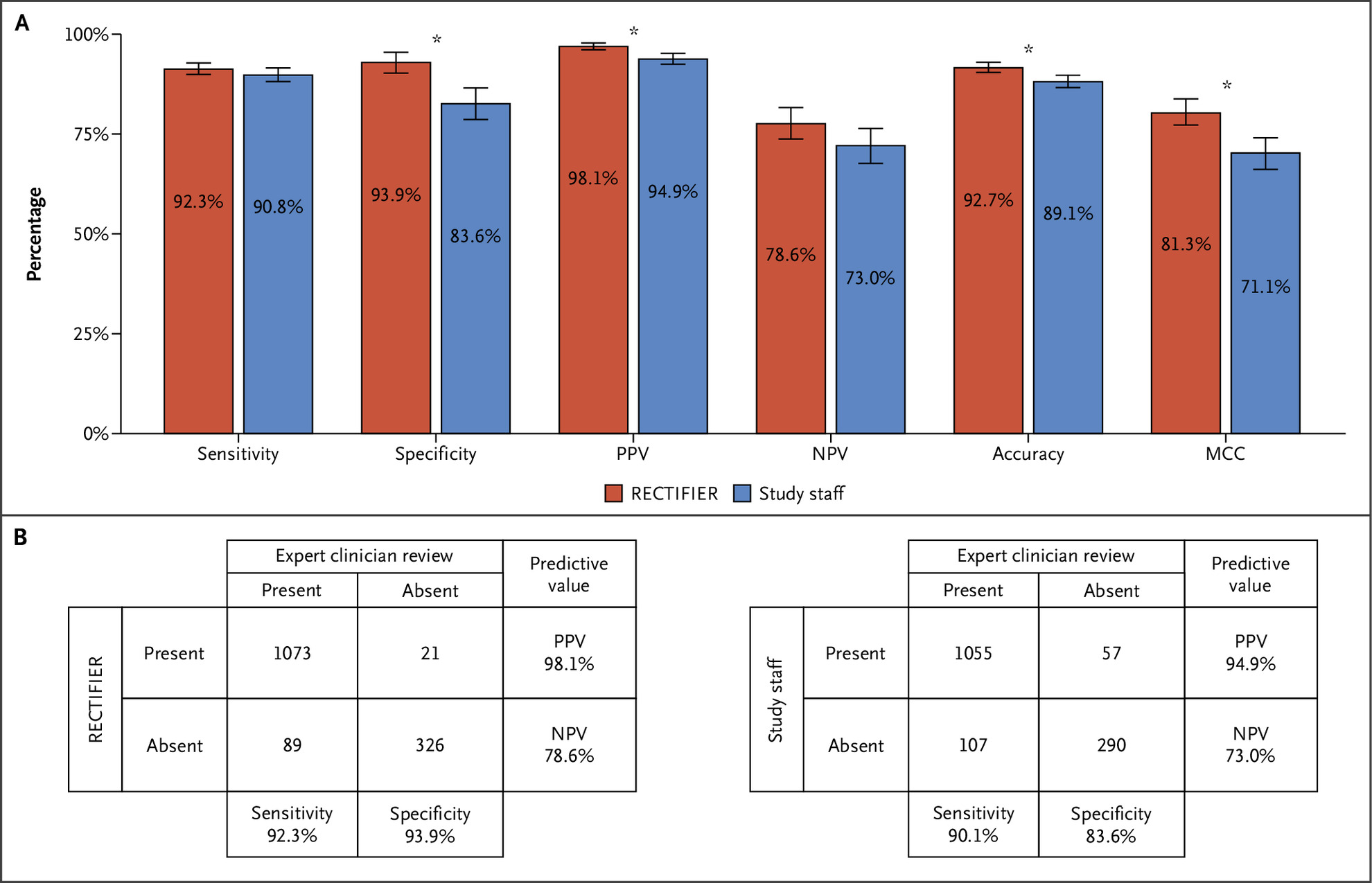
Panel A shows the performance metrics of RECTIFIER. Panel B shows the confusion matrices of RECTIFIER.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
While RECTIFIER offers an efficient and cost-saving strategy for clinical trial screening, potential hazards must be considered. These include loss of nuanced patient context, operational hazards due to system downtime, overlooked critical clinical details, potential inequity, and performance sensitivity to changes in data capture and clinical processes. Although RECTIFIER did not show statistically significant differences across racial or ethnic groups, directional differences could prove significant at scale. Therefore, integrating GPT-4 into clinical trial screening requires a careful balance between embracing technological advancements and mitigating associated risks.
Scalability and Future Applications
The modular design of RECTIFIER allows for scalable patient processing. It can handle large groups of patients by splitting them into manageable batches, enabling parallel execution on multiple servers. Each patient’s data is stored independently to prevent data contention and simplify retrieval. This scalable approach ensures that as the patient population grows, the workload can be managed efficiently.
Beyond clinical trials, RECTIFIER could also identify opportunities to address gaps in the quality of care, guideline-directed medication use, and population health management. However, its performance should be tested separately before being used for these applications at scale.
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
This study had several strengths, including the use of a large number of patients with coded inclusion and exclusion criteria ascertained by study staff and an expert clinician. The extensive dataset from an ongoing randomised clinical trial ensured that the findings were grounded in practical, real-world scenarios. However, there were limitations, such as the study cohort consisting predominantly of patients with a high prevalence of heart failure, which might lead to variable results when applied to other conditions.
Conclusion
Large language models like GPT-4 have the potential to significantly improve the efficiency and reduce the costs of clinical trial screening. However, it is essential to consider potential hazards and deploy appropriate mitigation strategies before fully automating the screening process. As we continue to refine these technologies, we must ensure their applicability across a spectrum of clinical scenarios while addressing potential challenges.
