Introduction
In cancer survivorship research, there is a growing call for a shift towards a health equity research agenda. This agenda aims to address the structural drivers of disparities. Consequently, this article reviews the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Cancer Survivorship Research Portfolio from 2017 to 2022. The goal is to assess how well this shift has been realised.
Key Findings
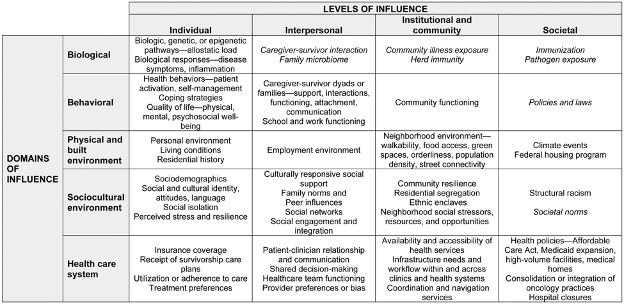
Among the 724 grants analyzed, 147 focused on health disparities within cancer survivorship. Notably, a significant proportion of these grants (73.5%) centered on survivors from racial and ethnic minority groups. This focus highlights the disparities prevalent in healthcare access and quality. The predominant grant type was observational (51.0%), with a considerable focus on individual-level influences (82.3%). Furthermore, the emphasis on survivors from minority groups underscores the need for targeted interventions. While the health care system domain (57.8%) and behavioural factors (51.0%) were well-represented, the research of the physical environment influences was relatively limited (12.2%).
Focus on Structural Drivers
Researchers must continue to advocate for inclusive and comprehensive research. Moreover, this research should focus on multifaceted drivers of health disparities among cancer survivors. By prioritising research on underrepresented populations and expanding the scope to include a wider range of cancer types, the field can make significant strides towards eliminating health inequities in cancer survivorship. Also, by embracing a holistic approach to research, focusing on social determinants of health, and considering the intersectionality of factors influencing health outcomes, researchers can discover novel insights that can inform more targeted interventions and policies to address disparities effectively. For instance, addressing structural drivers such as federal and state health policies, racism, and discrimination can have a profound impact. These factors create, perpetuate, or amplify health inequities. Moreover, the neighbourhood environment, quality of care, social engagement, cultural support, and resilience also play crucial roles.
Importance of Behavioural Factors
Nearly half of the grants measured or intervened upon drivers of health disparities on the behavioural domain at the individual level. Addressing cancer survivors’ modifiable risk behaviours related to smoking, alcohol use, nutrition, physical activity, and sleep remains important. These behaviours are directly linked to morbidity, premature mortality, and health disparities. However, promoting behavioural change alone is insufficient. Researchers must also consider the resources, opportunities, and the social, cultural, societal, and built environment context. These factors allow cancer survivors to engage in and sustain modified health behaviours.
Future Directions
Future research should aim to integrate multisectoral collaborations across various service sectors such as parks, recreation, food systems, commerce, and housing to address structural and social determinants of health disparities among cancer survivors. By engaging community-based organizations and leveraging the resilience of survivors and community assets, researchers can develop evidence-based interventions that enhance health outcomes. Moreover, researchers, policymakers, and healthcare providers must advocate for inclusive strategies that prioritise equitable access to healthcare services, ensuring that all survivors have equal opportunities for high-quality care. Future research can illustrate how market dynamics influence disparities and inform policies that promote fairness and equity in healthcare delivery, ultimately gaining health equity for all cancer survivors.