
Introduction
In an era of rapid medical advancements and an increasing volume of research information, the healthcare industry faces the challenge of keeping up with the latest developments. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare has emerged as a potential solution to this problem. Medical AI technology not only has the potential to enhance the efficiency and quality of medical services but also to address the shortage of healthcare providers, particularly in rural areas. This article explores the application of medical AI and its impact on improving access to healthcare.
The Power of AI in Healthcare
With the exponential growth of medical information, it is virtually impossible for healthcare professionals to stay completely up-to-date without assistance. AI technology offers a promising solution by leveraging machine learning and natural language processing capabilities to analyze vast amounts of data. IBM Watson, a leading AI healthcare support system, exemplifies the potential of this technology. By reviewing patients’ electronic health records (EHRs) and analyzing medical research publications and guidelines, Watson assists doctors in making efficient decisions. In a double-blind study, the system’s recommendations were found to be concordant with those made by a tumor board, but in a fraction of the time.
Addressing Healthcare Disparities in Rural Areas
The shortage of skilled healthcare providers in rural areas is a pressing issue in developing countries. Various factors contribute to this disparity, including a lack of students with a rural background, low wages, poor working conditions, and limited opportunities for professional development. Additionally, the overall shortage of healthcare workers exacerbates the problem. In developing countries, rural residents account for a significant proportion of the population, with Asia and Africa being home to 90% of the global rural population. India and China alone account for a substantial portion of this population. The doctor-to-population ratio in rural areas of these countries is significantly lower compared to urban areas, highlighting the need for innovative solutions.
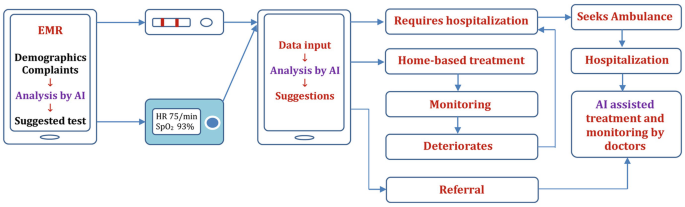
The Multilevel Medical AI Service Network
To address the challenges faced by healthcare systems in rural areas, a multilevel medical AI service network is proposed. This network comprises a frontline medical AI system at the basic level, regional medical AI support centers at the middle level, and a national medical AI development center at the top level. By implementing this network, healthcare providers in rural areas can access AI technology and receive support from regional centers, ultimately improving the availability and quality of healthcare services.
Conclusion
By leveraging AI’s analytical capabilities and providing support to healthcare providers, AI systems like IBM Watson can enhance decision-making processes and bridge the healthcare gap. The proposed multilevel medical AI service network further strengthens the potential of AI in improving healthcare access and quality, offering a promising solution to address the challenges faced by healthcare systems worldwide.
