
The World Bank Group (2017) estimates that at least half of the world’s population lacks access to basic healthcare. Moreover, nearly 100 million people are plunged into poverty annually due to healthcare expenses. These gaps in health provision are notably severe in low-income countries (LICs), where the majority of those facing impoverishing health expenses reside.
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) – defined as the global aim to ensure everyone receives the health services they need without suffering financial hardship – has been proposed as a solution to this pressing issue. The World Health Organisation (WHO) conceptualizes UHC as a ‘cube’ comprising three key dimensions: population coverage, service coverage, and financial risk protection.
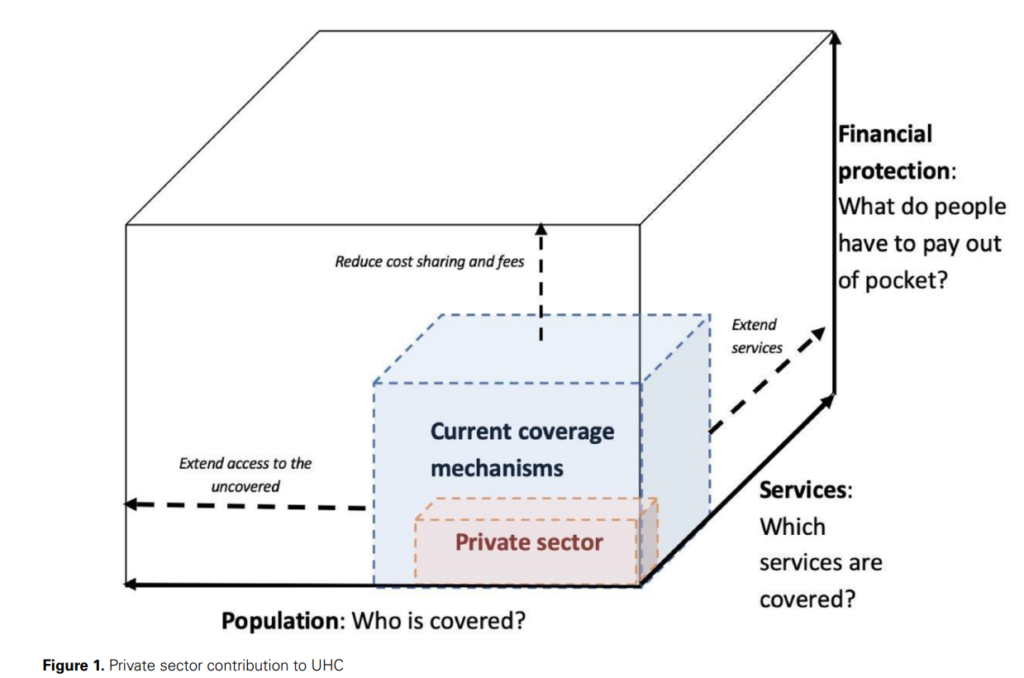
Source: Authors’ own elaboration, adapted from Kutsin (2013) and the WHO UHC cube (World Health Organisation, 2010; Kutzin, 2013).
However, the role of private healthcare in achieving UHC remains a subject of ongoing debate. While the public and private health sectors interact and shape each other’s performance, the unclear boundaries between the two make it difficult to define a UHC role for the private sector.
Private-for-profit (PFP) providers, motivated by commercial interests, and private not-for-profits (PNFPs), usually driven by philanthropic motives, are the two main types of private healthcare providers. The central role of profit in PFPs has ignited debate on their ability to adequately serve the poor and whether they can be contracted by governments to advance UHC goals.
The informal sector in LICs, which includes traditional birth attendants and healers, unlicensed drug shops, and market stalls, provides a substantial proportion of healthcare, particularly for the poor. However, the quality of care in both the public and private sectors in LICs often falls short, particularly at the lower end of the market.
A recent study extends the debate on the role of private healthcare in LICs by systematically reviewing recently published literature. They found that while formal private providers typically operate in already well-served urban settings, informal and not-for-profit ones cater to patients in underserved rural areas and generally at the lower end of the health market.
However, improving the quality and financing of informal providers may be key to expanding UHC in LICs. Given their ubiquitous nature and diversity of contributions, mechanisms for (self) accreditation will need to be strengthened to guarantee a minimum level of service quality from these actors.
Quality and effectiveness should be considered core principles of universal coverage and represent an additional dimension of the UHC cube in its own right.