Introduction
In the complex landscape of Multiple Sclerosis (MS) treatment, biosimilars have begun to play a crucial role. These biologic medications, highly similar to existing approved biologics, offer no clinically meaningful differences in terms of quality, safety, or efficacy. Understanding the impact of biosimilars on MS treatment is vital, especially in the context of cost reduction and improved patient access to therapies.
What Are Biosimilars?
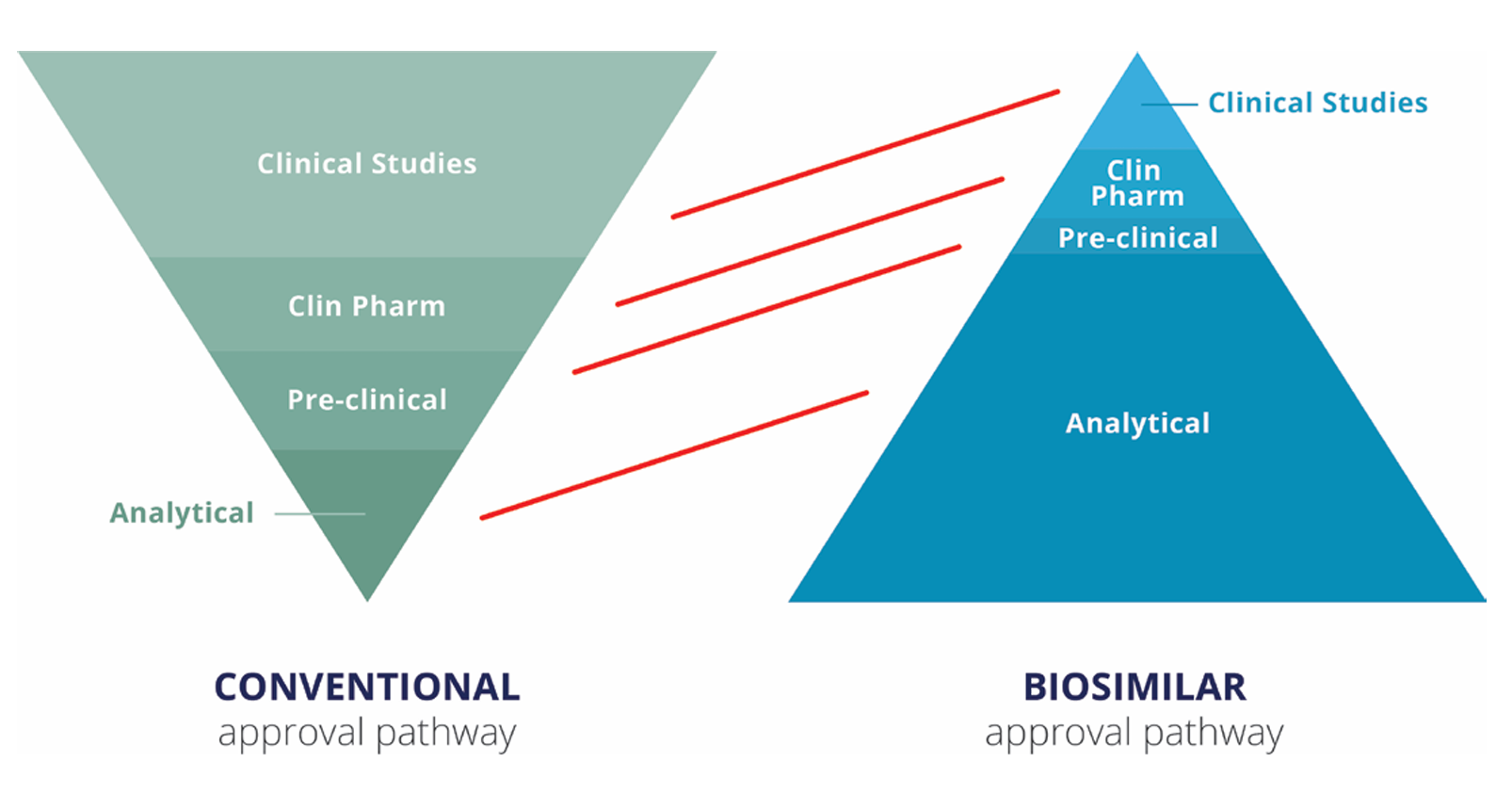
Biosimilars are biologic medications designed to be highly similar to an already approved reference product. They are made using the same types of living sources and have the same administration route, strength, dosage, potential treatment benefits, and potential side effects. Unlike generics, which are chemically synthesised and mostly small molecules, biosimilars are larger, structurally complex molecules. They undergo rigorous testing to demonstrate biosimilarity, including head-to-head comparability studies (Figure 1).
The Financial Impact of MS Care
MS is the second most expensive chronic condition, with lifetime direct medical costs estimated at $4.8 million. The high and increasing cost of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) is the single largest driver of healthcare expenditure in MS care. Biosimilars, being generally less expensive to develop due to an abbreviated clinical trial program, offer a promising solution. From 2017 to 2026, the use of biosimilars is expected to reduce direct spending on biologics by $54 billion, or approximately 3% of the total estimated biologic spending.
Benefits of Biosimilars
Biosimilars offer several benefits that extend beyond cost reduction. They increase the number of available treatment options and improve access to affordable healthcare. Affordability is a significant reason for the lack of access to MS therapy. By reducing the cost of high-value medicines, biosimilars relieve pressure on the healthcare system. Regulatory authorities require biosimilars to meet the same high standards of quality, safety, and efficacy as reference medicines, ensuring that patients receive effective treatment.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the benefits, there are concerns regarding the adoption of biosimilars. Patients and clinicians may express uncertainty about switching from a reference product to a biosimilar. The fear of negative effects, known as the “nocebo” effect, can also deter patients from switching. To address these concerns, it is essential to reassure patients about the biosimilar’s effectiveness and safety. Clinicians must take the time to educate patients about biosimilars, including the development process and supporting clinical trial data.
Clinical Data on Biosimilars
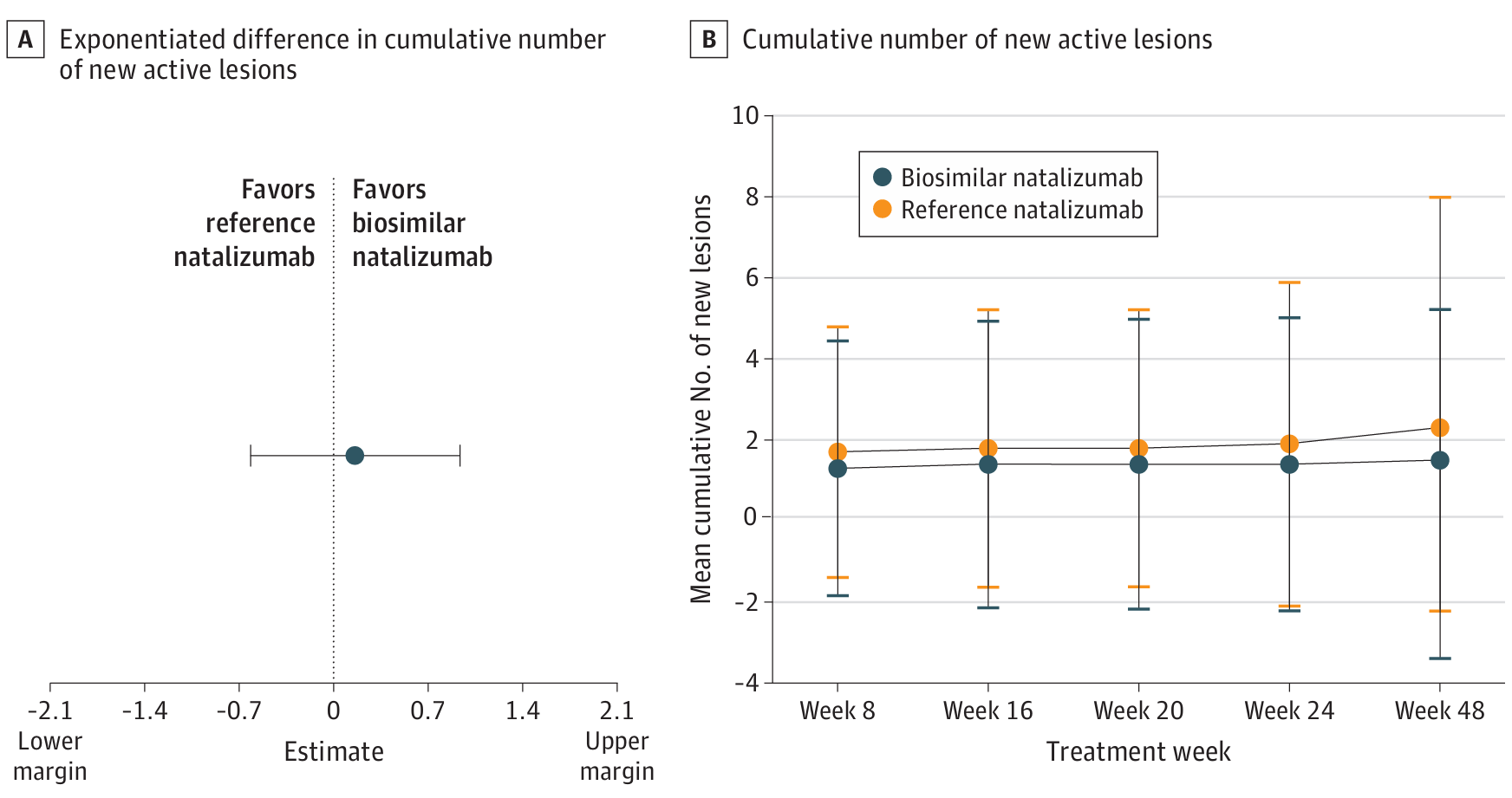
The clinical data on biosimilars is robust. For instance, a phase 3 study of a natalizumab biosimilar showed no clinically relevant difference in the mean cumulative number of new active lesions between treatment groups (Figure 2). Safety findings were also comparable between the biosimilar and the reference product. Such data reinforce the reliability of biosimilars in MS treatment, providing confidence to both clinicians and patients.
Educating Patients About Biosimilars
Educating patients about biosimilars is crucial in reducing anxiety about switching. Information should be provided early, especially if switching is considered. Clinicians should define biosimilars and share experiences with their use in other disease areas such as rheumatoid arthritis. Emphasising that biosimilars are not a new mechanism of action and that they have the same indications and dosing as originator agents can build patient confidence. Using the right terms and avoiding the word “generics” is also important.
Conclusion
The introduction of biosimilars in MS treatment marks significant progress. These medications are more affordable and potentially more accessible options than reference DMTs. Demonstrated by the “totality of evidence,” biosimilars offer the same benefits and safety profiles as their reference products. Clinicians need to take responsibility to educate patients and provide information about biosimilars. By doing so, we can ensure that patients receive the best possible care while alleviating the financial burden on the healthcare system.
