
Introduction:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly gaining traction in the healthcare sector, particularly with regards to disease prediction and detection. One specific example of application is the prediction of Cardiac Amyloidosis (CA) in patients with Aortic Stenosis (AS) undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR). Due to cost and testing burden, most TAVR patients with severe AS do not undergo CA assessment. An AI algorithm may identify a subgroup of individuals with a poor prognosis and assist with managing the risk factors in a cost-effective manner.
Understanding Cardiac Amyloidosis:
Aberrant protein (amyloid) infiltration characterises CA, a condition that increasingly prevails with age. This condition negatively affects patient outcomes, leading to heart failure and conduction abnormalities. Research reveals that CA affects up to 16% of patients with AS who undergo TAVR. However, assessing CA in all TAVR patients is difficult and costly, and not regularly done.
Artificial Intelligence in Predicting Cardiac Amyloidosis:
AI’s role in disease detection is expanding rapidly. It has been applied to the Electrocardiogram (ECG), a tool used to measure the rate and regularity of heartbeats, to screen and detect CA. ECG continues to be a cost-effective and readily accessible point-of-care test. A recent study indicates that using an AI algorithm to analyse ECGs can help identify patients with a worse prognosis and a higher chance of having undetected CA. This can be done using a simple and cost-effective method. An AI algorithm applied to pre-TAVR ECGs can identify patients with an increased probability of CA, which can lead to better patient selection for targeted clinical evaluation.
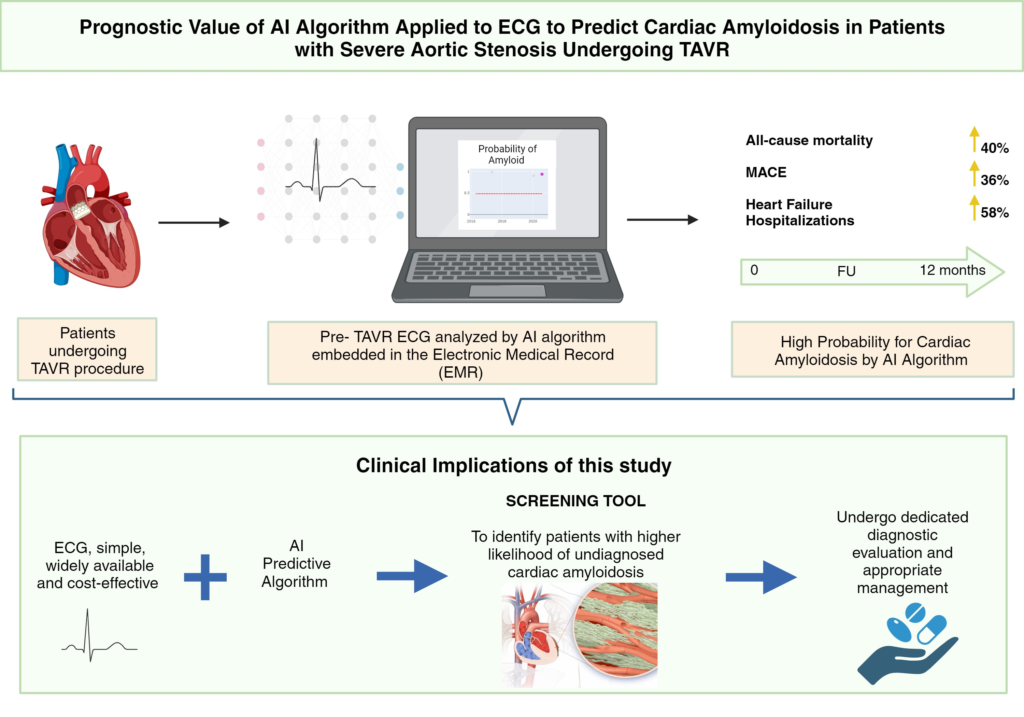
The Value of AI in Predicting CA:
The predictive value of AI in identifying CA is significant. AI advances offer unmatched capabilities to predict cardiovascular pathology from seemingly regular tests. Initially, a convolutional neural network (CNN) model was developed to detect and forecast atrial fibrillation from ECGs in normal sinus rhythm. Grogan et al. developed and validated an AI algorithm to predict CA from routine ECGs. The CA ECG predictive model used an ideal probability threshold of 0.485, with sensitivity of 0.84 and specificity of 0.85. The model assumes that ECG abnormalities in CA occur before clinical symptoms and that AI can improve CA detection probability in ordinary clinical ECGs. This suggests that AI could be a useful tool for screening and identifying higher-risk patients.
The Future of AI in Healthcare:
Continuous advancements in AI present unique opportunities for predicting cardiovascular pathology, even from tests that seem normal to human observers. This study takes the lead in analysing the AI-predicted risk of CA in ECGs of patients undergoing TAVR. It also explores the relationship between these predictions and actual cardiovascular outcomes. The findings suggest that AI could serve as a cost-effective screening tool. It could identify a patient subgroup that might require further diagnostic evaluation for CA.
Conclusion:
AI’s role in healthcare continues to evolve, offering promising potential in disease detection and prediction. In the context of TAVR patients, AI applied to pre-TAVR ECGs can identify a subgroup at high risk for CA who have worse clinical outcomes. This highlights the potential of AI as a screening tool, paving the way for more targeted diagnostic evaluations and better patient outcomes.
