Antimicrobial drug resistance is a growing public health problem, particularly in relation to respiratory tract infections (RTIs) which are commonly treated in primary care. Antibiotic resistance is linked to primary care antibiotic prescribing and has significant cost implications. Despite a decrease in consultation and prescription rates for RTIs from the late 1990s to early 2000s, antibiotic use has fluctuated, rising again during the COVID-19 pandemic. Children have higher consultation rates for RTIs and are often prescribed antibiotics, even when these prescriptions are at their lowest. There is limited evidence to support the use of antibiotics for chest infections in children, and differences between adults and children mean adult-derived evidence cannot be directly applied. Both parents and clinicians have concerns about illness progression and potential adverse outcomes. The study aimed to assess the effectiveness of amoxicillin in children with uncomplicated lower respiratory tract infection.
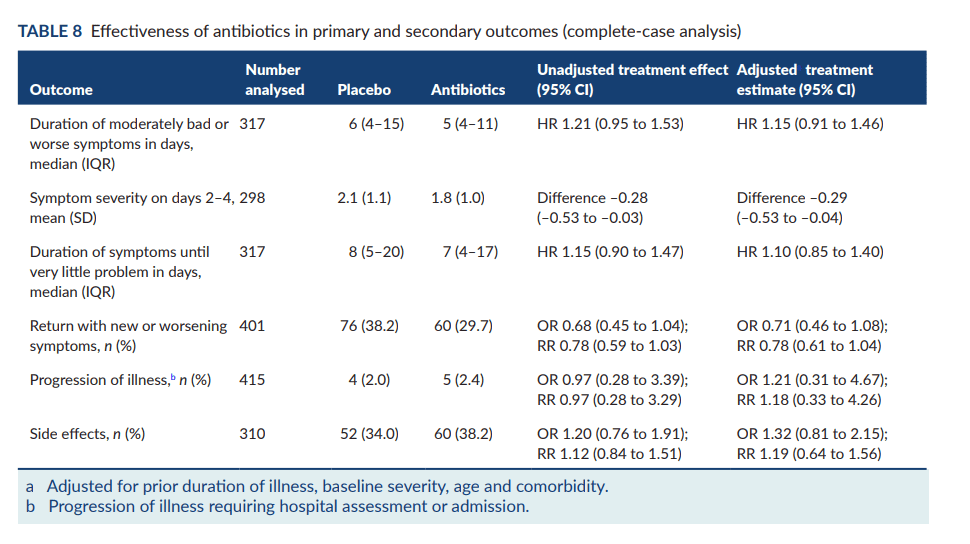
A total of 432 children participated in this study- found that amoxicillin for uncomplicated lower respiratory tract infections in children is unlikely to be clinically effective or to reduce health or societal costs. The duration of symptoms was similar in the antibiotic and placebo groups, as were the rates of consultations, illness progression, and side effects. The costs per child to the NHS were slightly higher for antibiotics, but there was no difference in non-NHS costs. The study concluded that parents need better access to information and clear communication about managing their child’s illness. Clinicians also noted a reduction in parents’ expectations for antibiotics.
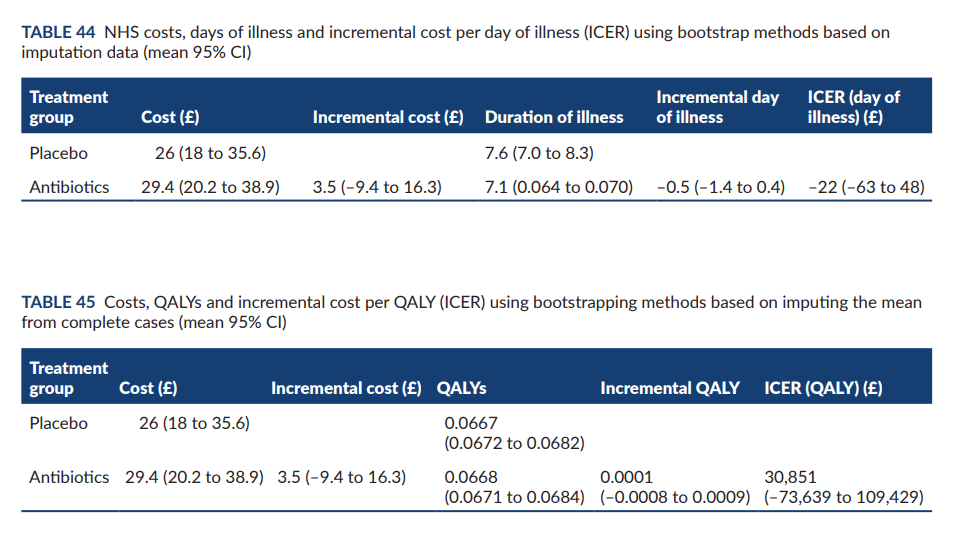
The study also found that the costs to the NHS per child were similar for both antibiotics and placebo (£29 vs £26), and societal costs were the same (£33). In the study they suggest that GPs should support parents to self-manage at home and provide clear communication about when and how to seek medical help. Parents whose children received antibiotics reported symptoms as moderately bad or worse for 5 days, while those given a placebo reported symptoms for 6 days. Side effects were similar in both groups. The study concluded that amoxicillin for chest infections in children is unlikely to be effective, and recommended that GPs support parents to self-manage at home while providing clear communication about when and how to seek medical help.