
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) stands as a chronic, severe autoimmune disease that affects multiple body systems. Its significant morbidity, mortality, and substantial burden on healthcare systems underscore the urgency for effective management strategies. This article unpacks the role of a novel therapeutic agent, Anifrolumab, in managing SLE, focusing on its economic impact and clinical efficacy.
SLE: A Burden to Patients and Healthcare Systems
SLE’s prevalence is notably high in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), with increasing epidemiological burden. The global epidemiological investigation revealed a prevalence rate of 166.92 per 100,000 individuals. SLE patients experience significant physical and psychological distress, affecting not only them but also their caregivers. The disease’s economic burden is evident, with high healthcare resource utilisation and substantial productivity loss due to patients’ mental and physical health deterioration.
The High Cost of SLE Flares
Exacerbations or flares of SLE increase the risk of organ damage (especially with nephritis) and the financial burden of the disease. They constituted 77.5% of hospitalisations among patients with SLE, with an average duration of hospital stay of 8.79 days. High flare frequency also leads to work productivity loss, further escalating the economic impact of SLE. The yearly healthcare expenses for all causes in the SLE cohort were about twice as high as those for non-SLE individuals. The costs were $17,270 for SLE and $8,350 for non-SLE. In addition, individuals with SLE undergo a more pronounced decline in their quality of life (QoL). This is as a result of depression, impaired mental well-being, and physical restrictions.
Anifrolumab: A New Hope in SLE Management
Anifrolumab, a pioneering type I interferon (IFNs) receptor antagonist, shows promise as an additional therapy for adults with moderate-to-severe active autoantibody-positive SLE. Moreover, clinical trials have confirmed its efficacy and safety. Therefore, it holds the potential to lower disease activity and enhance patients’ QoL.
Anifrolumab: A Cost-effective Solution
SLE management begins with targeting low-level disease activity state and limiting glucocorticoid (GC) reliance or chronic use to minimise adverse drug reactions. Many chronic illnesses use treat-to-target (T2T) therapy techniques. These techniques adjust treatment to achieve a clinical goal. In adults with active autoantibody-positive SLE of moderate-to-severe nature, doctors often use anifrolumab as add-on treatment. Compared to other SLE treatments like belimumab, anifrolumab proves to be cost-effective. It reduces disease activity and the utilisation of glucocorticoids, thereby fulfilling some unmet needs of SLE patients.
Anifrolumab in systemic lupus erythematosus management
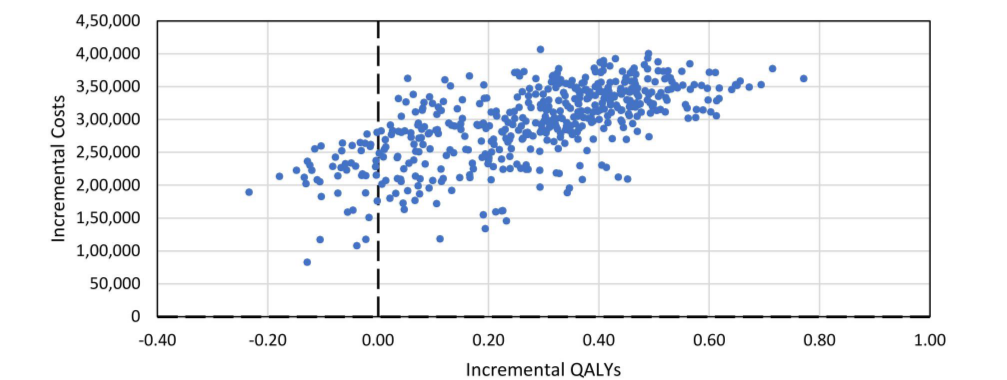
Bruce et al. conducted an indirect treatment comparison (ITC) between anifrolumab 300 mg and belimumab 10 mg/kg. They administered these treatments to adult SLE patients alongside conventional therapy. Their study revealed that patients treated with anifrolumab were twice as likely to achieve a ≥ 4 point reduction in their systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index (SLEDAI) score at 52 weeks. This was in comparison to those treated with belimumab. The research compared the incremental cost-effectiveness ratios (ICERs) of anifrolumab with belimumab IV and belimumab SC. The ICER for anifrolumab was AED 466,371 compared to belimumab IV. When compared to belimumab SC, it was AED 252,612. These ICERs fall below the cost-effectiveness threshold in the UAE. While the current research on Anifrolumab’s efficacy and cost-effectiveness holds strengths such as clinical trial data and sensitivity analyses, limitations exist. These include the lack of country-specific evidence and head-to-head comparisons between Anifrolumab and other treatments.
Conclusion
Anifrolumab offers a cost-effective option for managing adult patients with active, autoantibody-positive SLE in the UAE. Its potential to reduce complications and organ damage, and improve patients’ quality of life, makes it a promising addition to standard SLE treatment protocols.
