Introduction
A significant challenge faced by hospitals and medical practitioners in low- and middle-income countries is the lack of sufficient healthcare facilities for timely medical diagnosis of chronic and deadly diseases. Maternal and neonatal morbidity due to non-communicable and nutrition-related diseases is a serious public health issue that leads to several deaths every year. Detecting these conditions at their early stages is challenging, putting patients at risk of developing severe conditions over time. However, the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has opened up new possibilities for improving maternal and neonatal health. This article will give an overview on AI’s Approaches to Maternal and Neonatal Health in Low Resource Settings.
AI holds Promise for Maternal and Neonatal Health
AI has emerged as a practical assistive tool in various healthcare sectors, but its application in maternal and neonatal health is still in its nascent stages. One example of how AI can be used in low-resource settings is in maternal health and diagnostics services. In these settings, access to proper healthcare infrastructure and professionals is limited, making it difficult to provide holistic care to pregnant women and their children. However, AI technologies such as digital chatbots and support groups can aid in maternal and neonatal health monitoring and management. These technologies can engage users in follow-up questions about their health in their desired language, helping to disperse basic health information.
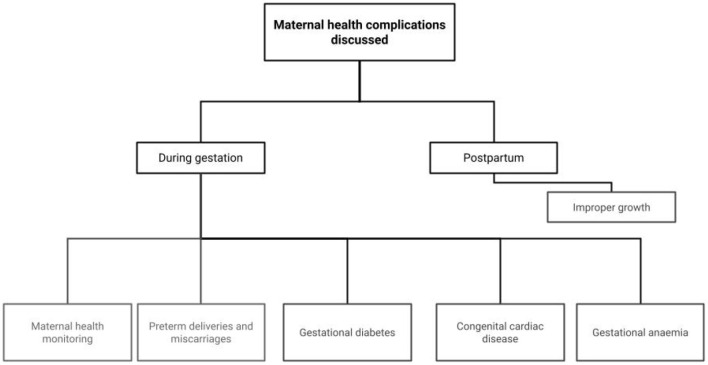
Figure 1: Focus Areas on Role of AI in complimenting maternal health
Challenges and Solutions for AI
Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) or Dependable AI (DAI) can provide insights into the decision-making process of AI models. This level of explainability increases the confidence that medical practitioners and AI researchers have in the system, leading to broader adoption of AI in the healthcare field. By understanding why someone has been classified as ill or otherwise, the perception of AI models as a “black box” can be changed, making them more scalable and employable. XAI can be merged with smart healthcare systems that incorporate the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and AI, particularly in the fields of maternal and neonatal health. These intelligent healthcare systems can be utilized for various purposes, including disease diagnosis and treatment selection.
In some crucial small sample size healthcare problems where large datasets are not available, Few-shot learning or Zero-shot learning can be used to train AI models. These learning frameworks utilize domain information to reach medical decisions or predictions, making them efficient tools for doctors to handle rare medical conditions and problems that require years of experience.
Conclusion
Improving maternal and newborn health requires bringing speedy diagnosis and treatment to point-of-care settings in developing nations with limited resources.
