Introduction
Wearable devices, such as smartphones, smart bands, and smartwatches, are now being used to detect Atrial fibrillation (AF), offering non-invasive and instantaneous access to patients. Moreover, voice technology, through voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant, is emerging as a valuable tool for remote monitoring and the provision of medical services in cardiology. These advancements in AI-driven clinical decision making with medical devices are transforming the way cardiovascular diseases are diagnosed and managed. AI in cardiology and medical devices have pioneered how personalised our healthcare can be.
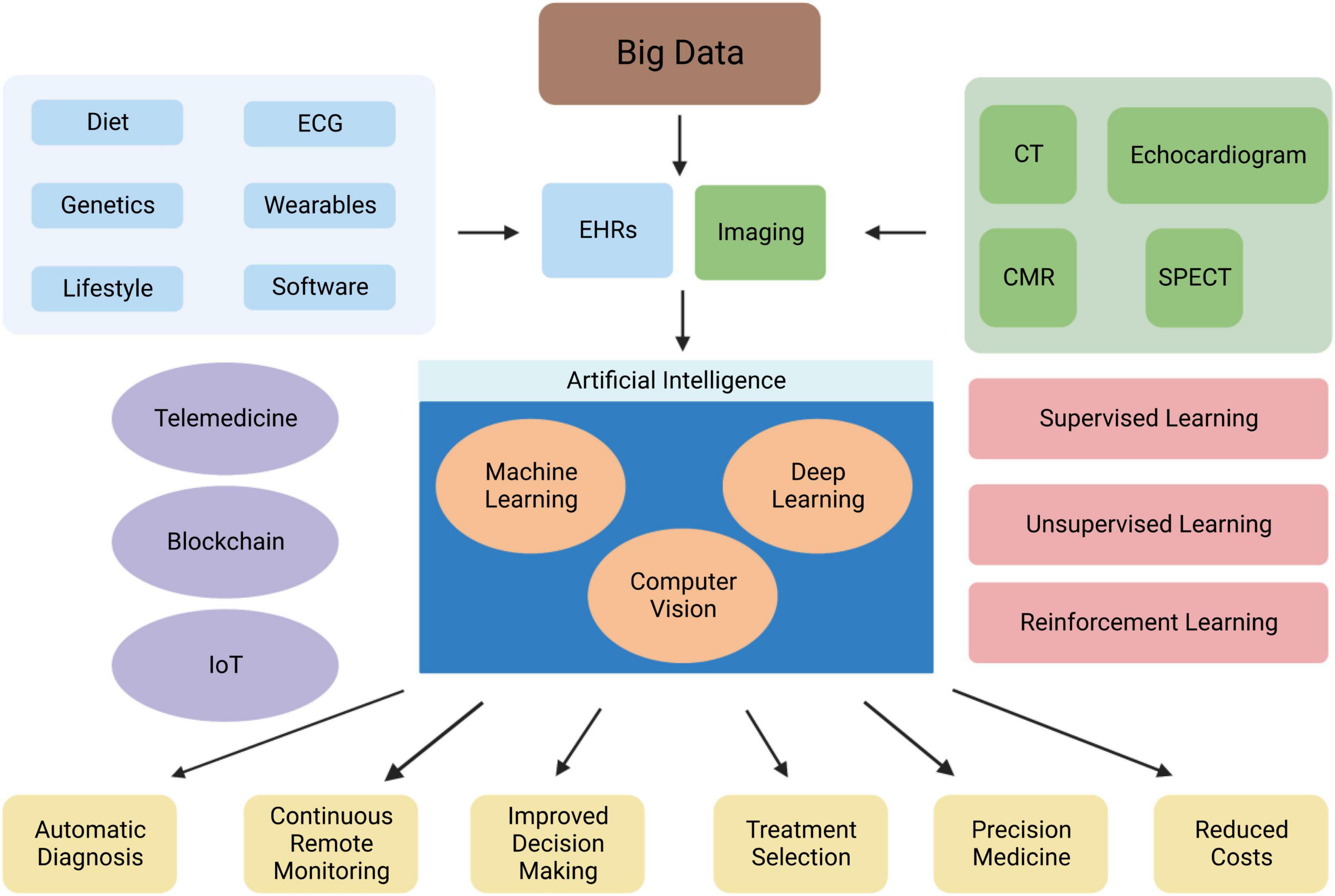
Wearable Devices for AF Detection
AF detection can be challenging due to the limitations of current diagnostic methods. However, advancements in technology have paved the way for the use of wearable devices in detecting AF. These devices, such as smartphones, smart bands, smartwatches, earlobe sensors, and handheld electrocardiogram devices, offer non-invasive and instantaneous access to patients.
The Apple Watch and AliveCor are notable examples of wearable devices that enable uninterrupted monitoring and individual analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. The KardiaBand from AliveCor, a smartphone application based on machine learning (ML), has been developed for the recognition of AF from an ECG. In a randomized controlled trial (RCT) of AF screening, the AliveCor Kardia monitor connected to a WiFi-enabled iPod successfully detected AF in ambulatory patients aged 65 and above at high risk of stroke. This screening method proved to be more effective than routine monitoring over a 12-month period.
Smartphone Utilization in Identifying Subclinical AF
The Apple Heart Study demonstrated the effectiveness of smartphones in identifying patients with subclinical paroxysmal AF. With data from 420,000 participants, the study detected irregular pulses in 0.5% of patients, 34% of whom were diagnosed with AF confirmed by ECG. Participants who received notifications about their irregular pulse had a higher likelihood of commencing anticoagulant or antiplatelet treatment. A significant number of patients diagnosed with AF underwent further interventions such as cardioversion, implantable loop recorder placement, anti-arrhythmic medication initiation, and ablation.
Voice Technology for Remote Monitoring and Medical Services
Voice technology, through voice assistants like Amazon’s Alexa or Google Assistant, has gained popularity for mainstream use. These advanced software architectures, based on neural network techniques, enable speech recognition and generate human-like responses. Voice assistants are now being utilized as emerging tools for remote monitoring and the provision of medical services.
In the field of cardiology, voice applications have proven to be valuable. For instance, the Mayo Clinic First Aid skill provides medical guidelines, including cardio-pulmonary resuscitation instructions. The CardioCube voice application facilitates paperless medical history taking in outpatient cardiology clinics, generating accurate reports.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into cardiology through medical devices has developed the detection and management of AF. Wearable devices, such as smartphones and smartwatches, offer non-invasive and instantaneous access to patients, allowing for continuous monitoring and analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. Voice technology has emerged as a valuable tool for remote monitoring and the provision of medical services in the field of cardiology.
