
Introduction
The accurate identification and timely updating of adverse reactions in drug labelling are critical for patient safety and effective drug use. Postmarketing surveillance plays a crucial role in identifying previously undetected adverse events (AEs) that emerge when a drug is used in broader and more diverse patient populations. Traditional methods of updating drug labelling with new AE information have been manual, time-consuming, and error-prone. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) created and validated the LabelComp tool. This innovative artificial intelligence (AI) tool enhances the efficiency and accuracy of postmarketing drug safety surveillance.
The Importance of Accurate Drug Labelling
Drug labelling provides healthcare professionals with a summary of essential scientific information needed for the safe and effective use of a drug. When a drug is approved, its known adverse reactions are included in the drug’s labelling. Real-world usage after a drug’s approval involves larger and more diverse patient populations compared to pre-approval clinical trials. Therefore, it is important to revise the Full Prescribing Information to provide accurate, up-to-date information on drug safety.
Prior research into safety-related labelling changes has explored the frequency and timing of safety issues and related labelling changes. These studies show that the majority of products have a new safety issue added after approval, and these updates continue throughout a drug’s lifecycle. However, previous efforts to characterise safety issues identified and added after approval have been tedious and time-consuming, involving manual comparisons of updated drug labelling with previous versions.
Introducing the LabelComp Tool
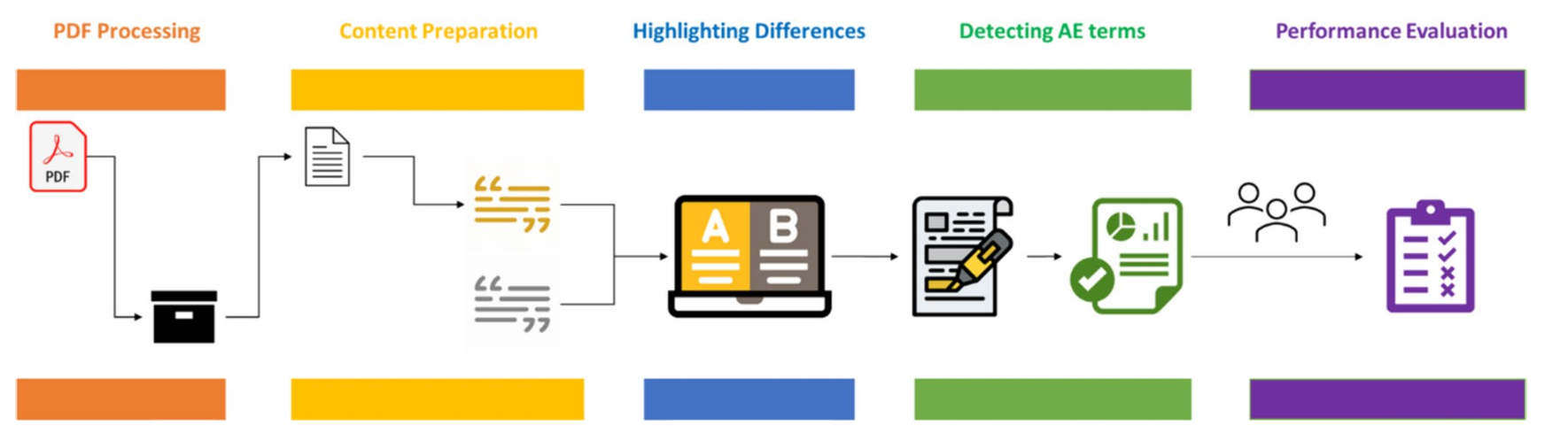
The LabelComp tool supports the comparison of FDA labelling documents within a web interface designed to identify product safety labelling changes. It has two main components. The first component uses text analytics to extract all texts from the two drug labelling documents being compared. The textual differences identified between the drug labelling documents are then highlighted to facilitate human expert review.
The second component leverages AI, specifically a Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model, for natural language processing. The LabelComp tool uses the RxBERT model, a domain-specific BERT model developed by our group, which is based on BioBERT, with additional training on prescription drug labelling documents curated from FDALabel. RxBERT detects and highlights AE changes and their locations within specific sections of drug labelling documents. These sections include Boxed Warnings, Contraindications, Warnings and Precautions, Adverse Reactions, and Drug Interactions.
Validation and Performance Evaluation
To determine the accuracy of the LabelComp tool in identifying safety-related labelling changes, researchers performed a validation study. Their goal was to create and validate a tool with high accuracy that could enable researchers and FDA reviewers to efficiently identify safety-related labelling changes.
The validation study of 87 drug labelling PDF pairs demonstrates the tool’s high accuracy. The F1 scores of overall performance ranged from 0.795 to 0.936 across different evaluation tiers, and the recall was at least 0.997, with only one missed AE out of 483 total AEs detected. This high recall indicates that LabelComp can identify nearly all newly added AEs, making it a significant advancement in drug safety surveillance.
Furthermore, one author conducted a post-hoc validation analysis by reviewing labels from 53 drugs approved by CDER in 2020. This analysis generated similar F1 scores across the three tiers and a recall of 1, confirming the tool’s high sensitivity.
Conclusion
The LabelComp tool is a significant contribution to pharmacovigilance, automating the identification of AE changes in drug labelling documents. Leveraging advanced AI techniques, including the RxBERT model for natural language processing, LabelComp effectively addresses the challenges of manual labelling comparison. Our validation study demonstrated LabelComp’s high accuracy in detecting new AEs in drug labelling, achieving a recall rate of 0.997.
As an open-source tool, LabelComp allows researchers to use, improve, and share enhancements with the public. You could adapt parts of the code to support other review or regulatory science activities. For example, the function that converts a PDF drug labelling document into machine-processable text is valuable. The ability to identify AEs in document sections also has potential for other uses.
LabelComp automates AE identification and provides detailed comparison outputs, marking a significant advancement despite its limitations. It doesn’t capture all AE changes and requires human validation for quality assurance. The FDA will continue developing and iterating AI tools for drug safety review and research. This aligns with its broader mission to use AI and emerging scientific approaches to advance regulatory science and public health.
