Introduction
Patients with lung cancer often face a grim prognosis, with nearly half being diagnosed at an advanced stage. The 5-year survival rate for lung cancer varies significantly, ranging from 9% to 64% depending on the cancer stage. For years, lung cancer has remained the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. Recent studies, including the SYMPRO-Lung trial, have explored the use of patient-reported outcome (PRO) symptom monitoring to improve health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in these patients.
Understanding PRO Symptom Monitoring
PRO symptom monitoring involves patients reporting their symptoms, which are then used to guide clinical care. The SYMPRO-Lung trial was the first to demonstrate that a patient-initiated (reactive) approach to PRO symptom monitoring was as effective as a physician-initiated (active) response in improving HRQOL 15 weeks after treatment initiation. This was a pragmatic cluster randomised trial. This patient-centred approach could potentially reduce the workload for healthcare practitioners (HCPs) while maintaining clinical efficacy.
Long-Term Effects of PRO Symptom Monitoring
The study extended the observation period to one year to assess the long-term effects of weekly online PRO symptom monitoring. The trial involved 515 lung cancer patients across 14 hospitals. Results indicated that both reactive and active approaches significantly improved long-term HRQOL. Notably, the reactive approach, which involved sending alerts directly to patients, was less labour-intensive for HCPs.
Survival Benefits and Challenges
Previous studies have shown survival benefits with active PRO symptom monitoring. However, these studies often required additional resources, such as funded nursing staff. The SYMPRO-Lung trial did not find significant differences in progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) between the intervention and control groups. The lack of statistical significance could be attributed to the study’s limited power and the flexibility given to patients in the reactive group to decide whether to contact their HCPs.
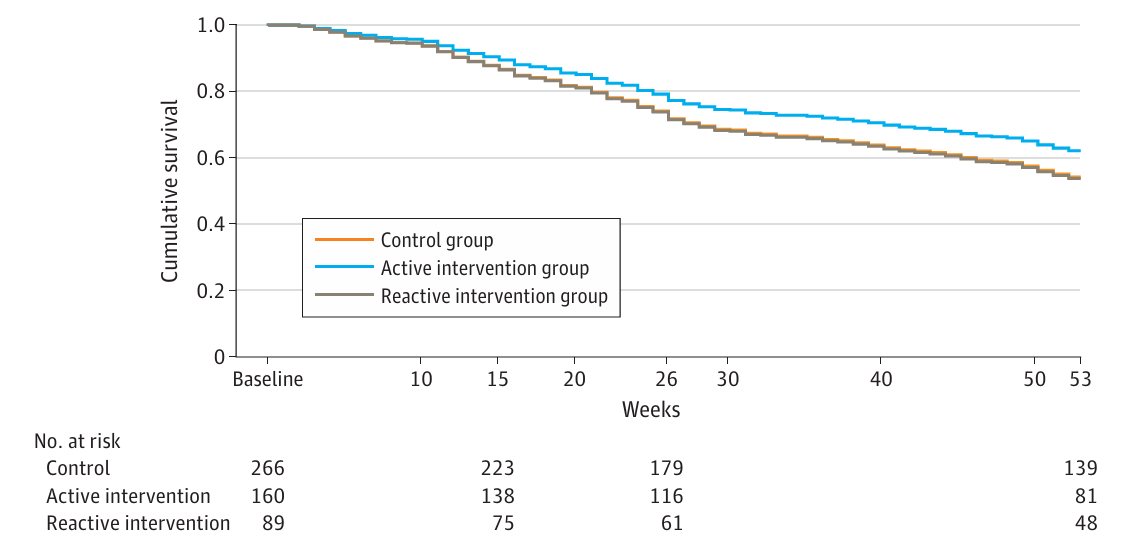
Response to Patient-Reported Symptom Monitoring vs Care as Usual (Control)
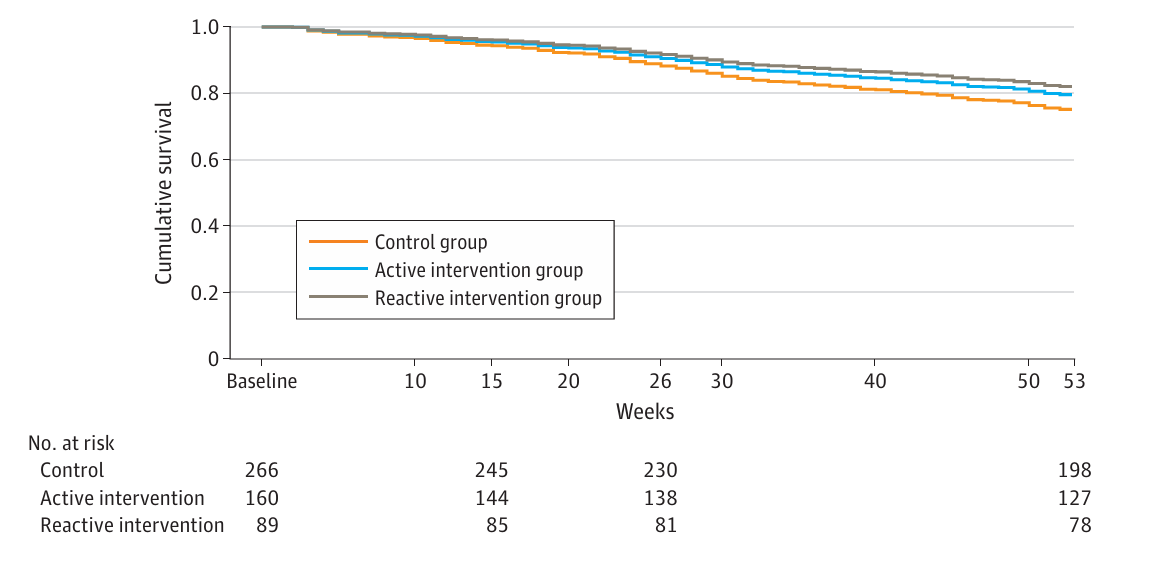
Patient-Reported Symptom Monitoring vs Care as Usual (Control)
Strengths and Limitations
One of the strengths of this study is its pragmatic design, which allowed for the adaptation of the intervention to the specific workflows of each participating hospital. This broad-scale, multicenter approach enhances the generalisability of the findings. However, the study also had limitations, such as differences in patient characteristics between groups and potential selection bias due to the online nature of the intervention. Future research should focus on addressing these limitations and improving algorithm accuracy to minimise false-positive alerts.
Conclusion
The SYMPRO-Lung trial demonstrates that PRO symptom monitoring can improve long-term HRQOL in lung cancer patients. The reactive approach, where patients initiate contact with their HCPs, proved to be as effective as the active approach and less labour-intensive. While no significant survival benefit was observed, the findings justify further research into the implementation of symptom monitoring in routine lung cancer care. Both reactive and active approaches offer flexibility for HCPs and patients, potentially leading to more sustainable and cost-effective care models.
