
Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA), a prevalent joint disease affecting over 7% globally, leads to chronic pain and reduced mobility. Various factors, including ageing and genetics, contribute to its progression. With cases doubling to 527.8 million globally, OA poses a significant socioeconomic burden, particularly in knee and hip joints. Despite increasing prevalence rates, OA management is often overlooked, necessitating efficient resource allocation for effective treatment. Cost-effectiveness in OA treatments is crucial for optimising healthcare resources. Osteoarthritis management through health economics and health technology assessment (HTA) plays a crucial role in guiding policymakers towards optimal decisions.
Overview of the management of OA
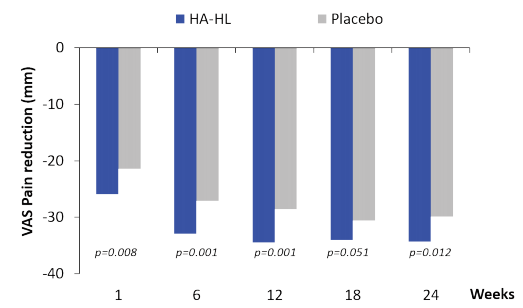
Current OA treatment strategies combine pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, emphasising personalised care for symptom control and improved quality of life. Symptomatic slow-acting drugs, analgesics, and intra-articular treatments are recommended by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO), with a focus on balancing efficacy and safety. Among intra-articular treatments, the new high- and low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid (HA-HL) therapy for knee osteoarthritis has shown promising results in recent trials. A single intra-articular injection of HA-HL significantly reduced pain and improved functionality compared to placebo, with effects lasting up to 24 weeks.
Economic Evaluations of OA Interventions
Economic evaluations compare the costs and benefits of different healthcare interventions. They are essential for ensuring that limited resources are used efficiently. Hiligsmann et al. explored the economic evaluations of OA interventions, focusing on trial-based and model-based evaluations. In OA, these evaluations often measure the difference in societal costs against the difference in quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
- Trial-Based Evaluations
Trial-based evaluations collect patient-level data on costs and QALYs during randomised controlled trials. This method has high validity as it uses data from the same population. However, it has limitations, such as a truncated time horizon and restricted generalisability. For example, a 1-year trial may not capture long-term benefits.
- Model-Based Evaluations
Model-based evaluations use mathematical models to predict long-term health outcomes and costs. These models extrapolate beyond available evidence, allowing for indirect comparisons and generalisation to other settings. However, they are subject to uncertainties, such as parameter uncertainty and assumptions.
HA-HL Therapy from Swiss Healthcare Perspective
A recent randomised controlled trial assessed the cost-effectiveness of an innovative HA formulation for knee OA from a Swiss healthcare perspective. The study demonstrated that the HA-HL formulation was cost-effective compared to placebo, with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of 27,860 Swiss francs (CHF) per QALY gained. This ICER is significantly below the primary threshold of 91,540 CHF per QALY, which corresponds to US$ 100,000, as well as secondary thresholds of 79,423 CHF per QALY, based on Switzerland’s 2020 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, and 254,307 CHF per QALY, equivalent to three times the GDP per capita. Sensitivity analyses further validated these findings, showing that the ICER remained below all thresholds even when varying cost parameters, thereby confirming the robustness of the results.
Conclusion
HTA has an important role in shaping OA management decisions, emphasising the economic value of interventions. Economic evaluations offer insights into cost-effective treatment options, aiding policymakers in optimising patient care and reducing the socioeconomic burden of OA. Continued advancements in HTA methodologies will further enhance resource allocation decisions, ensuring efficient and equitable healthcare systems for OA management.
