
Introduction
Obesity stands as a significant risk factor contributing to the global burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), impacting health systems worldwide. The 2022 World Health Organization (WHO) European Regional Obesity Report highlights overweight and obesity as major risk factors for NCDs, with profound implications for health, disability, and mortality rates. In Türkiye, a concerning rise in obesity prevalence surpasses that of European counterparts, necessitating urgent measures to address this escalating public health issue. The economic impact of obesity in Türkiye is profound, affecting both individuals and the healthcare system. A recent study by Gogas Yavuz et al. explores the financial burden of obesity-related comorbidities (ORCs) and provides insights into the healthcare costs associated with this epidemic.
Rising Prevalence of Obesity in Türkiye
Türkiye has the highest obesity prevalence among European countries. Approximately 32% of the population is living with obesity, while 61% are overweight. This alarming trend has surpassed many European nations and rivals the United States. The prevalence of obesity has increased significantly over the last few decades, highlighting the urgent need for effective interventions.
Health Implications of Obesity
Obesity is a systemic disease with widespread cardiometabolic effects. It is closely linked to insulin resistance, which often precedes type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In Türkiye, around 80% of patients with T2DM are also living with obesity. Furthermore, obesity is associated with various other health conditions, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, congestive heart failure, poor respiratory function, hypertension, and vascular diseases.
In a previous study from Türkiye, it was shown that obese women with coronary heart disease had a diabetes prevalence almost three times higher than non-obese women. Moreover, a higher body-mass index (BMI) was significantly related to increased plasma cholesterol and hypertension. These findings underscore the severe health consequences of obesity.
Economic Impact of Obesity-Related Comorbidities
The economic burden of ORCs in Türkiye is substantial. In 2012, NCDs accounted for 87.5% of all deaths among people aged 30–70 years. Of these, 36.6% were due to cardiovascular diseases, 7% to chronic respiratory diseases, and 5.8% to diabetes. In 2011, per capita healthcare expenditure in Türkiye was US$1160, with 70% of the government’s total health expenditure directed towards addressing NCDs.
ORCs accounted for 7.4% of total disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in Türkiye, translating to an economic burden of over US$17 million in 2015. This constituted 2.45% of the nation’s gross domestic product. Despite price control efforts, Türkiye’s Social Security Institution (SSI), the single public payer of pharmaceuticals, medical materials, and health services in Türkiye, faced a 10% annual rise in drug spending from 2012 to 2014, with health inflation peaking in 2022, exacerbating the financial burden of ORCs.
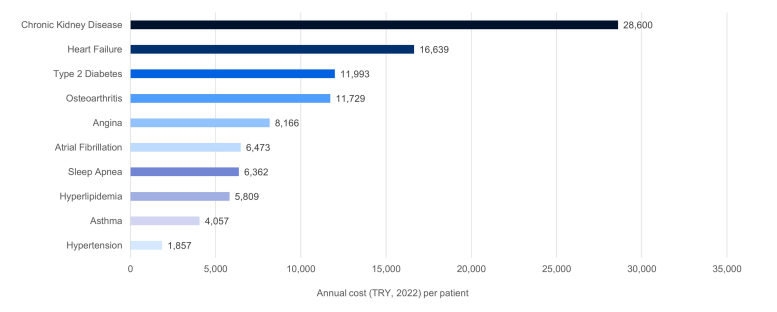
Micro-Costing Analysis of ORCs
This study estimated direct healthcare costs associated with ten ORCs in Türkiye by utilising a micro-costing approach. This method involved surveying 70 public sector physicians to assess healthcare resource use. Unit costs were derived from the SSI’s Healthcare Implementation Communique. The annual cost per patient per ORC was then calculated.
The analysis revealed that chronic kidney disease (CKD), heart failure, and T2DM are the costliest ORCs, incurring annual costs of 28,600 TRY, 16,639 TRY, and 11,993 TRY, respectively. Individuals with any ORC triggered direct healthcare costs ranging from 1857 TRY to 28,600 TRY annually. Understanding the cost drivers across different obesity-related complications reveals the substantial impact of treatment-related adverse events and inpatient procedures on healthcare expenditure.
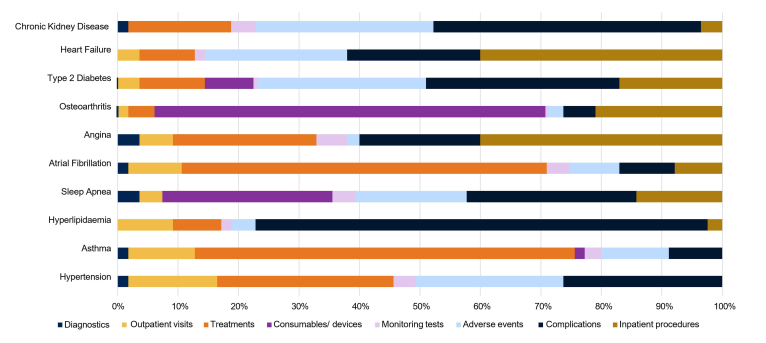
Conclusion
The economic impact of obesity in Türkiye is significant, with substantial financial burdens on the public healthcare system. Therefore, it is important to demonstrate the potential for cost savings through appropriate obesity interventions. Quantifying the burden of obesity across a comprehensive spectrum of ORCs provides valuable insights for the decision-makers in Türkiye. By leveraging micro-costing analyses and addressing evidence gaps, stakeholders can drive informed decisions and optimise healthcare investments to mitigate the impact of obesity on the public health system.
