
Introduction
Scoliosis, a spinal deformity impacting youths, poses multifaceted challenges, necessitating a deeper understanding for effective interventions. The prevalence of scoliosis, ranging from 0.20% to 3.10% globally, underscores the importance of understanding its nuances. Adolescent scoliosis, particularly, idiopathic, prevails among 80% of cases, predominantly affecting adolescents aged 10-18 globally. In China, the overall scoliosis prevalence was reported as 5.14%, with a recent surge attributed to academic stress and lifestyle changes among students. Huang et al. conducted a comprehensive study on the prevalence and risk factors of adolescent scoliosis among middle school students aged 10 to 17 in Gansu Province. Their findings provide valuable insights for the development of preventive strategies, especially targeted screening, which can improve efficiency, accuracy, and personalised prevention plans, leading to cost reduction, optimised healthcare resource allocation, and enhanced services in high-risk areas.
Exploring Adolescent Scoliosis in Gansu Province
Gansu Province, a diverse region in Northwest China, offers a unique landscape for studying adolescent scoliosis. With a population of 26.17 million across varied terrains and 44 ethnic groups, Gansu stands as a crucial focal point for epidemiological investigations into scoliosis among adolescents.
Data were collected using a paper-based survey. Surveyors conducted face-to-face interviews to gather demographic data, daily electronic device usage, sleep posture, family medical history, physical activity, dietary habits, and bodily pain. Orthopaedic physicians measured body-mass index (BMI), shoulder symmetry, scapular symmetry, waist symmetry, and pelvic tilt. Screening for scoliosis involved visual inspection, the Adams forward bend test, and trunk rotation angle measurement. The screening adhered to the International Society on Scoliosis Orthopaedic and Rehabilitation Treatment (SOSORT) guidelines.
Insights from Population Study
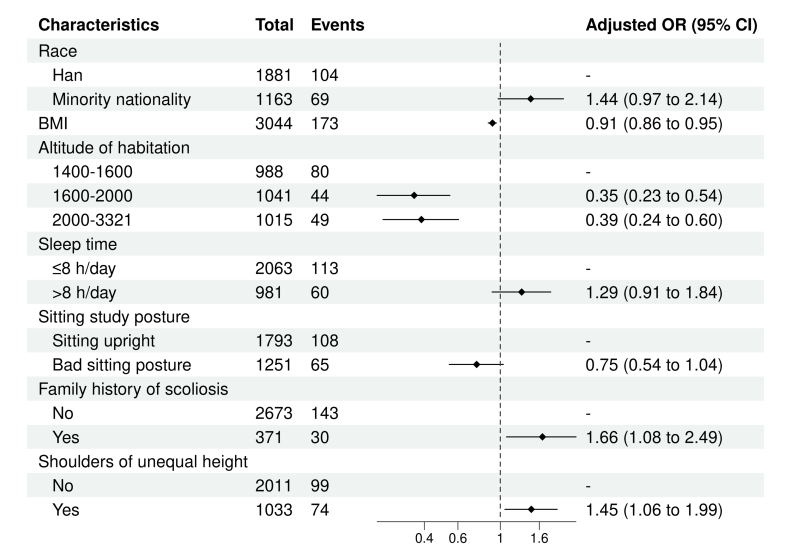
A population study encompassing 3,044 adolescents aged 10-17 unveiled a 5.68% prevalence of suspected scoliosis. Of the participants, 1,555 were males (51.08%) and 1,489 were females (48.92%). The prevalence was similar between males (5.53%) and females (5.84%). However, the prevalence peaked at 14 years for males (6.70%) and 15 years for females (8.75%). Moreover, factors such as BMI, family medical history, and altitude of habitation emerged as significant influencers. Notably, adolescents at lower altitudes (1,400–1,600 m) exhibited a higher prevalence compared to those at higher altitudes (1,600–3,321 m) (p < 0.001). Adolescents with scoliosis had lower BMI levels (p = 0.033) and a higher family history (17.34%, p < 0.001). Differences in scoliosis prevalence among different cities underscore the regional variations in scoliosis incidence, with Lanzhou City exhibiting higher rates.
Risk Factors in Adolescent Scoliosis
Logistic regression analysis identified several risk factors for adolescent scoliosis. These risk factors included age, BMI, gender, race, city, altitude of habitation, family history, sleeping posture, sleep time, daily electronic device usage, sitting posture for study, daily sitting time for study, regular exercise, habitual food preference, fruit consumption, and neck or shoulder or low back pain.
Public Health Implications and Future Directions
The findings on the prevalence and risk factors of adolescent scoliosis in Gansu Province serve as a solid foundation for shaping public health policies. Key factors such as genetic predispositions, low BMI, and shoulder imbalances have been identified as significant contributors to suspected scoliosis. However, the study’s limitations, including its cross-sectional design and absence of X-ray examinations, emphasise the need for further longitudinal investigations to establish causal relationships and definitive diagnoses. In conclusion, to manage the costs associated with adult scoliosis, which include disabilities, multiple surgeries, and the requirement for specialised equipment, it is crucial to promptly screen high-risk adolescents for suspected scoliosis, implement effective preventive and intervention strategies, and establish an integrated health education model involving schools, families, and hospitals.
