
Introduction
Endometrial cancer (EC) remains a significant health concern in the US, with 66,200 new cases and 13,030 deaths projected for 2023. The cost-effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) like pembrolizumab and dostarlimab in treating advanced EC is crucial for healthcare decision-making. A recent study published in Journal of Gynecologic Oncology examines the economic viability of these treatments, focusing on their impact on survival rates and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs).
The Burden of Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is the most common gynaecological malignancy in the US. Despite early-stage diagnosis in 67% of patients, 10-15% present with advanced disease, showing a 5-year survival rate of 15-17%. The prognosis varies significantly based on the molecular subtype of the tumour. Approximately 80% of patients have mismatch repair-proficient microsatellite-stable (pMMR-MSS) tumours, while 30% have mismatch repair-deficient microsatellite instability-high (dMMR-MSI-H) tumours.
Treatment Options and Survival Outcomes
First-line treatment for advanced EC typically involves carboplatin plus paclitaxel. However, the prognosis remains poor, with median progression-free survival (mPFS) and overall survival (mOS) rates of just 1 and 3 years, respectively. Recent advancements in ICIs, particularly pembrolizumab and dostarlimab, have shown promise in improving survival outcomes. Two large phase 3 trials, RUBY and NRG-GY018, demonstrated significant benefits of combining ICIs with chemotherapy.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Zhu et al. developed a model to compare the cost-effectiveness of dostarlimab plus chemotherapy (DC), pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy (PC), and chemotherapy alone. The model used a 20-year time horizon and considered various costs, including drug administration, follow-up, monitoring, and adverse event management. The primary outcomes included total costs, life-years (LYs), QALYs, and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER).
Key Findings
The analysis revealed that DC and PC treatments significantly improved survival outcomes compared to chemotherapy alone. For pMMR-MSS patients, DC treatment extended survival by 1.76 LYs and provided an additional 1.38 QALYs at an ICER of $234,527/QALY. In contrast, PC treatment extended survival by 0.31 LYs and provided an additional 0.23 QALYs at an ICER of $974,177/QALY.
For dMMR-MSI-H patients, DC treatment extended survival by 5.52 LYs and provided an additional 4.36 QALYs at an ICER of $135,165/QALY. PC treatment extended survival by 2.69 LYs and provided an additional 2.15 QALYs at an ICER of $266,423/QALY. The cost-effectiveness of DC compared to PC was $86,671/QALY for pMMR-MSS patients and $7,866/QALY for dMMR-MSI-H patients.
Based on recommendations from the World Health Organization (WHO) and prior publications, willingness-to-pay (WTP) threshold waws set to $150,000/QALY to assess the cost-effectiveness of DC and PC treatments for advanced EC. The findings suggest that DC is the most cost-effective option for the dMMR-MSI-H population and may also be justified for the pMMR-MSS population based on the health benefits it provides. A cost-effectiveness acceptability curve demonstrated that the cost-effectiveness of DC treatment increases as the WTP threshold is raised.
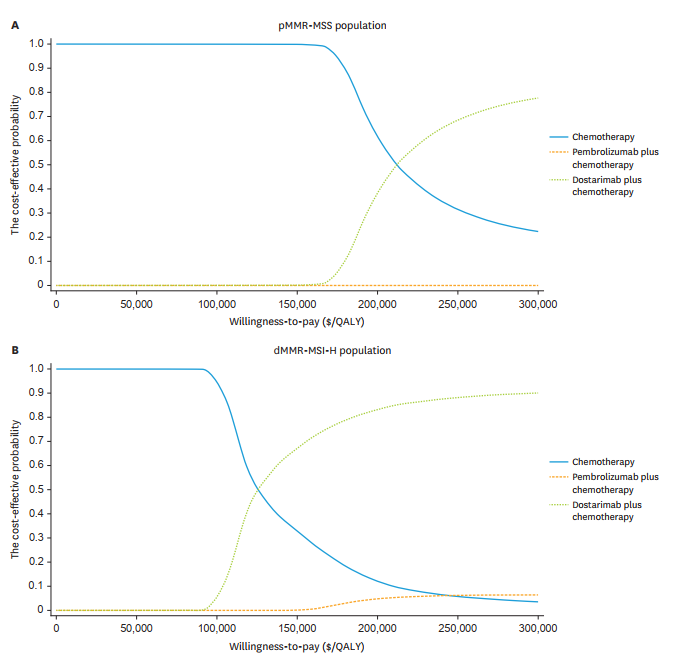
Sensitivity and Subgroup Analyses
Sensitivity analyses indicated that the prices of ICIs, costs of adverse event management, and risk of adverse events significantly influenced ICER results. However, these variables did not alter the overall conclusions. Subgroup analyses for the dMMR-MSI-H population showed consistent benefits across different patient groups.
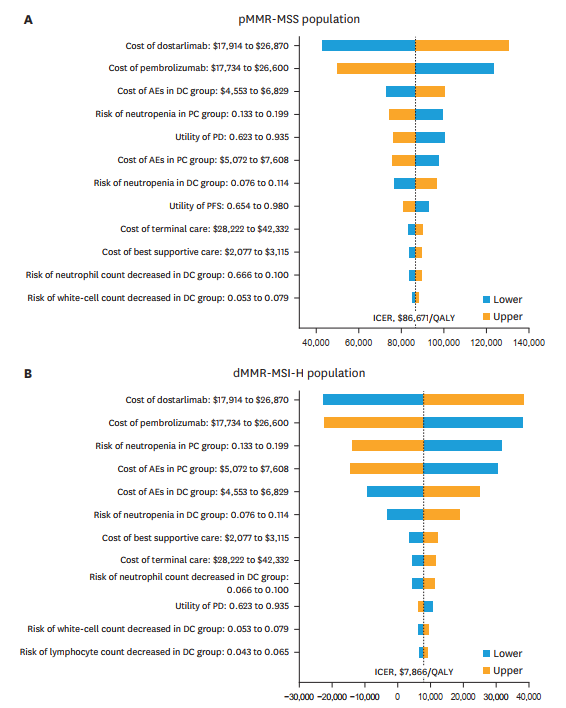
Conclusion
The cost-effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors in treating advanced endometrial cancer varies based on the molecular subtype of the tumour. While both DC and PC treatments offer significant survival benefits, DC appears more cost-effective, particularly for dMMR-MSI-H patients. These findings can guide clinicians, policymakers, and patients in making informed healthcare decisions.
