
Introduction
Precise risk assessment is of vital significance in the increasingly complex discipline of cardiovascular health. The development of the Predicting Risk of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Events (PREVENT) equations by the American Heart Association (AHA) in 2023 marks a significant shift from the previously established Pooled Cohort Equations (PCEs) of 2013. This article explores the differences between these two risk calculators. This includes their implications for primary prevention statin therapy and the potential impact on public health.
Understanding the PCEs and PREVENT Equations
The Pooled Cohort Equations (PCEs)
Introduced in 2013 by the AHA and the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the PCEs were designed to estimate the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). These equations take into account factors such as sex, race, age, cholesterol levels, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medication use, diabetes diagnosis, and smoking status. However, the PCEs have faced criticism for overestimating risk. This is seen especially among Asian and Hispanic populations. This is mostly due to the lack of diversity in the original cohorts used for their development.
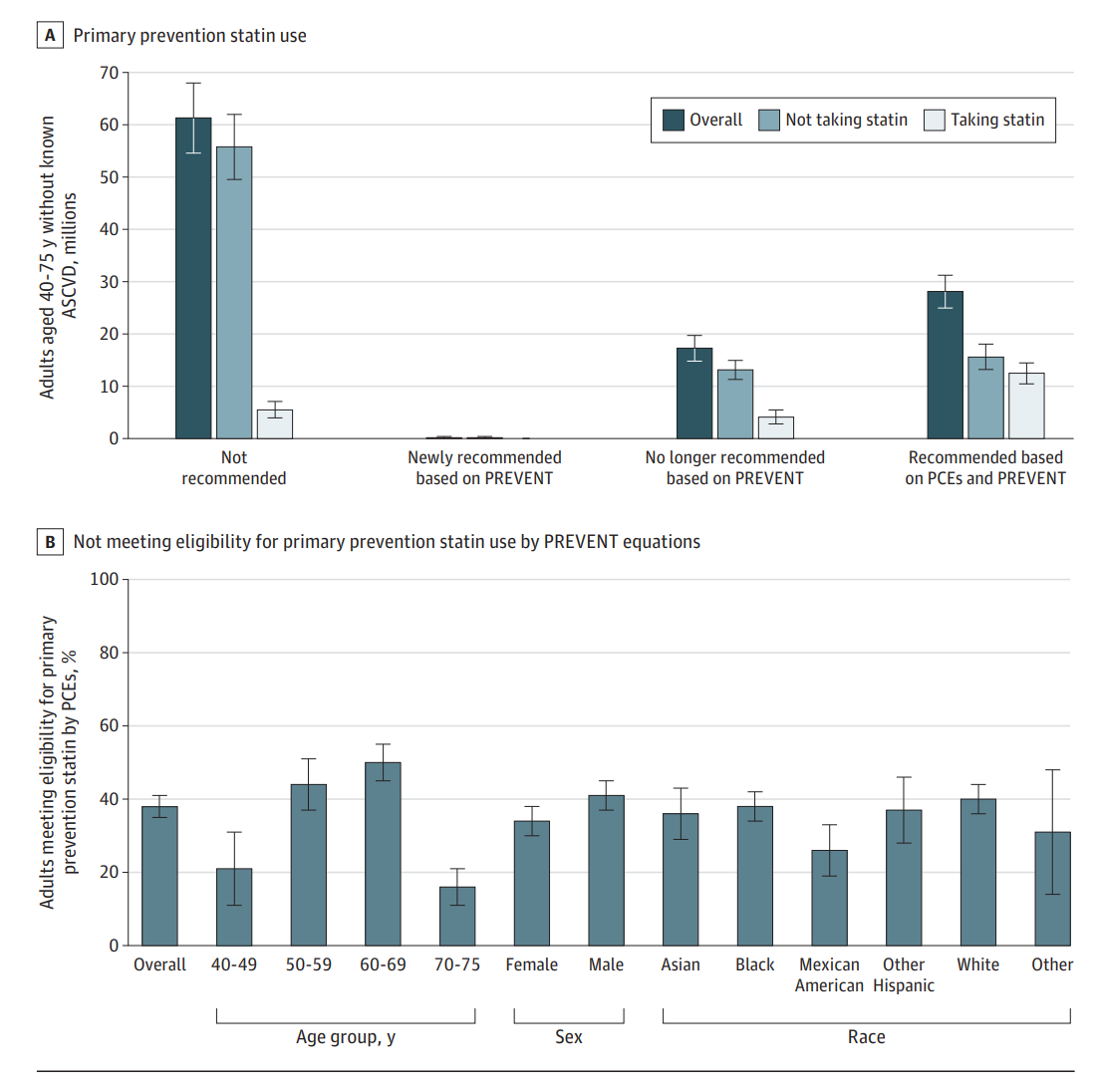
Disease Events (PREVENT) Equations on Recommendations for Primary Prevention Statin Use
The PREVENT Equations
The PREVENT equations, developed in 2023 by the AHA Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Scientific Advisory Group, aim to provide a more accurate risk assessment. They aimed to accomplish that by incorporating contemporary and diverse data sources. Unlike the PCEs, the PREVENT equations exclude race as a factor and include measures of renal function and statin use. Optional variables such as haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), and social deprivation index further refine the risk estimates.
Key Differences and Their Implications
Risk Estimates and Statin Eligibility
A study using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) revealed that the PREVENT equations significantly reduce the estimated 10-year ASCVD risk across various demographic groups compared to the PCEs. As a result, 17.3 million adults who were previously recommended for primary prevention statin therapy under the PCEs would no longer meet the eligibility criteria using the PREVENT equations. This includes 4.1 million adults currently taking statins.
Impact on Demographic Groups
The study found that the PREVENT equations led to larger declines in risk estimates among Black individuals and adults aged 70 to 75 years. This reduction in estimated risk could lead to fewer recommendations for preventive medication use, particularly among older adults, potentially reducing polypharmacy and its associated risks.
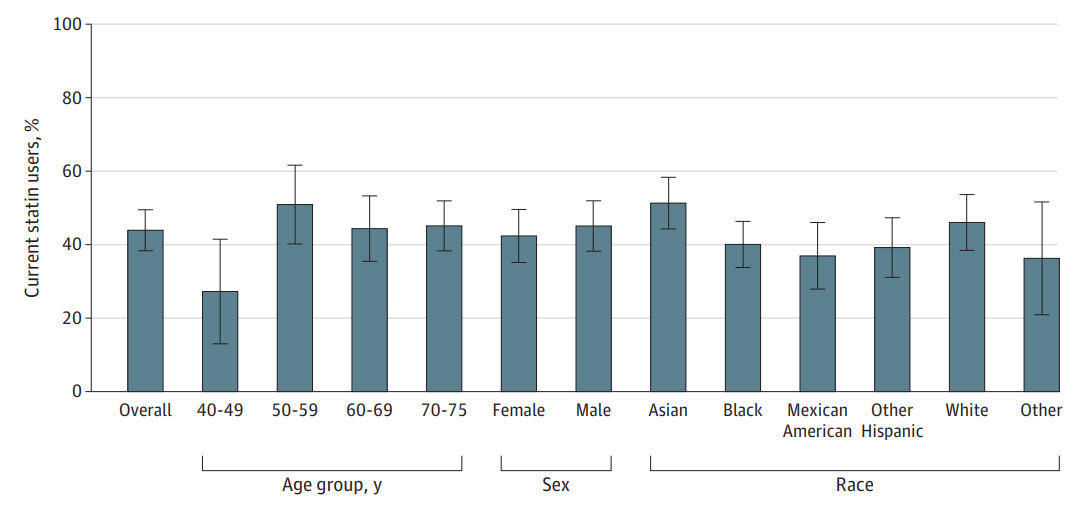
of Cardiovascular Disease Events (PREVENT) Equations Who Reported Current Statin Use
Policy and Practice Implications
Data Accuracy and Bias
The PREVENT equations are based on data from the Optum Data Warehouse. This is a large dataset derived from billing and electronic health records. While these data sources are more recent and comprehensive than those used for the PCEs, they are also more prone to errors. Underreporting of ASCVD events in disadvantaged subgroups could lead to underestimation of risk. Therefore, it is crucial to assess and improve data accuracy and reduce bias in electronic health records.
Moving Towards Shared Decision-Making
Given the uncertainties and potential inaccuracies in risk estimation, it may be beneficial to shift from precise treatment thresholds to recommendations that encourage risk communication and shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers. This approach would allow for more personalised and informed decisions regarding preventive therapies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the introduction of the PREVENT equations represents a significant advancement in cardiovascular risk assessment. By incorporating more diverse and contemporary data, these equations offer a more accurate estimation of ASCVD risk. However, the implications of these changes, particularly the reduction in statin eligibility, highlight the need for ongoing evaluation and adaptation of clinical guidelines. As we move forward, the focus should be on improving data accuracy, reducing bias, and fostering shared decision-making to enhance patient care.
