
Introduction
Preventive health programs, such as vaccination campaigns, wellness initiatives, and early screening programs, play a crucial role in enhancing public health and reducing healthcare costs. This article evaluates the long-term economic benefits of these programs through comprehensive analysis, employing cost-benefit analysis (CBA) and cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA).
Vaccination Campaigns
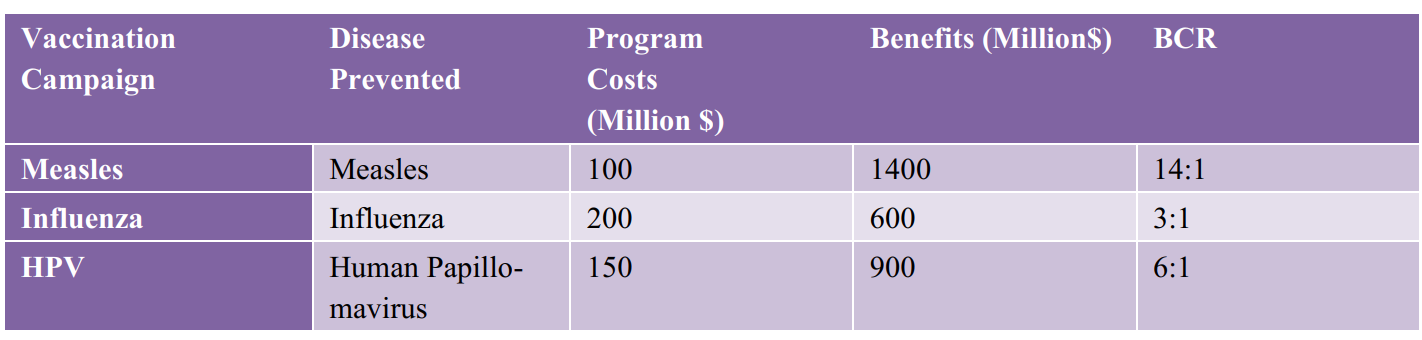
Vaccination campaigns have consistently demonstrated high benefit-cost ratios. For instance, the measles vaccination program has shown significant efficacy in preventing disease outbreaks and reducing healthcare expenditures. The economic benefits of vaccination campaigns are substantial, as they avert costly treatments and hospitalisations associated with preventable diseases.
Moreover, the HPV vaccination campaign has also demonstrated significant economic benefits, as highlighted in the study. With program costs amounting to $150 million, the benefits derived from the campaign reach $900 million, resulting in a benefit-cost ratio (BCR) of 6:1. This means that for every dollar spent on the HPV vaccination, there is a return of six dollars in economic benefits. These benefits include savings from prevented disease treatment and productivity gains, underscoring the economic efficiency and public health value of the HPV vaccination program.
Wellness Initiatives
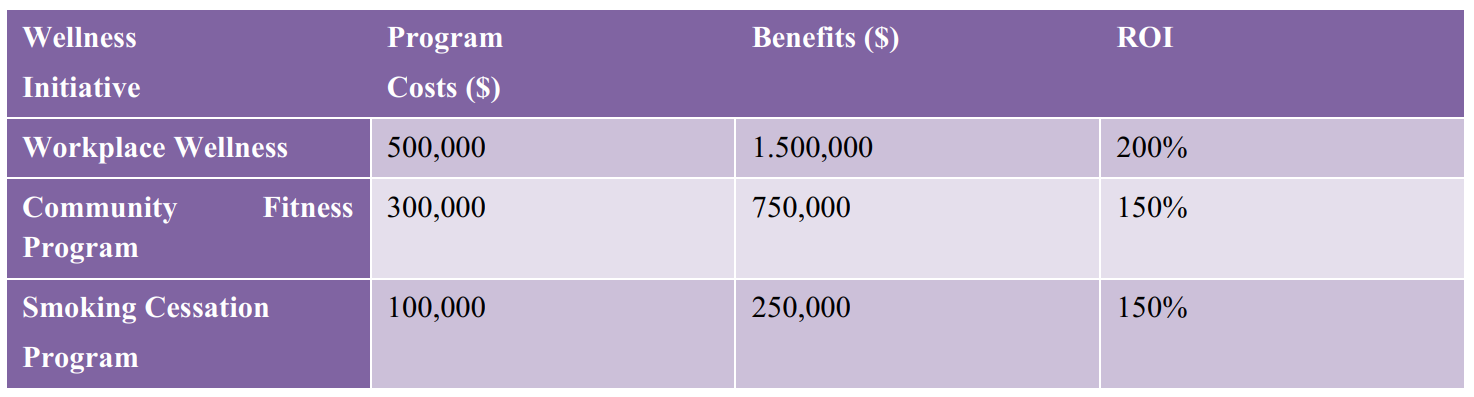
Wellness initiatives, particularly workplace wellness programs, yield remarkable returns on investment (ROI). Studies, including those by Baicker et al. (2010), report an average ROI of 3.27 for these programs. Wellness initiatives not only lead to direct healthcare cost savings but also enhance employee productivity, reduce absenteeism, and improve overall workplace morale. The average ROI of 200% underscores the importance of investing in employee health as a strategic approach to achieving long-term organisational success and economic benefits.
Early Screening Programs
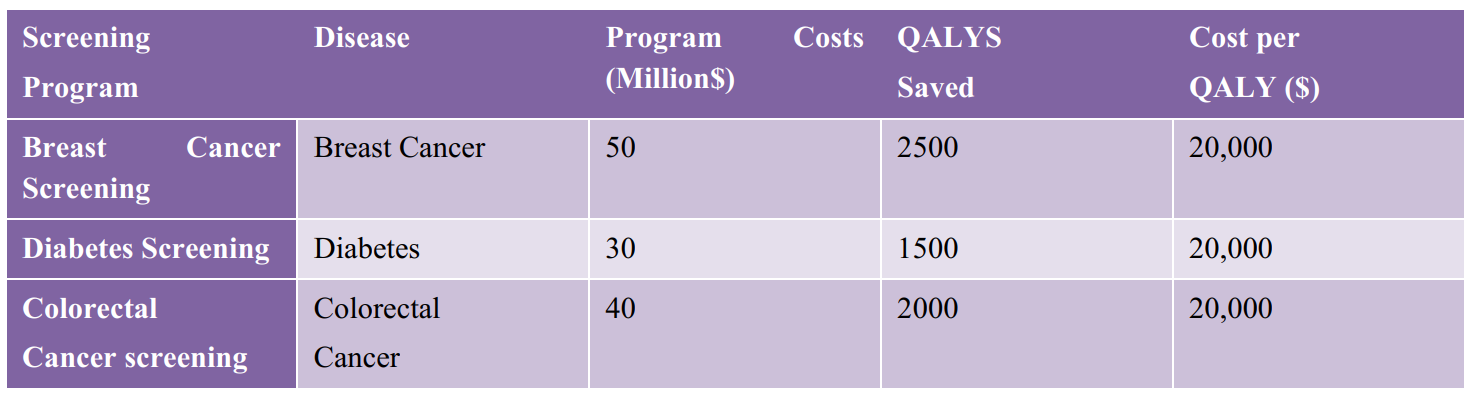
Early screening programs for diseases such as breast cancer and diabetes are highly cost-effective. The cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) of breast cancer screening revealed a cost per quality-adjusted life year (QALY) of $20,000. Early detection and treatment of diseases significantly improve survival rates and reduce treatment costs, providing substantial long-term savings for healthcare systems. The favourable cost per QALY indicates that early screening programs are not only economically efficient but also critical for improving health outcomes and quality of life for patients.
Comparative Analysis
Comparing the economic benefits across different types of preventive health programs shows that vaccination campaigns generally offer the highest benefit-cost ratios (BCR), while wellness initiatives provide substantial ROI, and early screening programs offer significant cost-effectiveness in terms of QALYs. The geographic distribution of studies further highlights the global applicability and effectiveness of these programs. Studies conducted in various regions consistently demonstrate the economic benefits of preventive health measures, reinforcing the universal value of investing in preventive strategies.
Policy Implications
The findings of this study have significant policy implications. Policymakers should prioritise funding and support for preventive health programs to maximise health and economic benefits. The robust economic returns from vaccination campaigns, wellness initiatives, and early screening programs justify sustained investment and policy support. By integrating preventive health strategies into national health policies, governments can achieve substantial healthcare cost savings, improve population health, and drive economic growth.
Conclusion
Preventive health programs offer substantial long-term economic benefits and are essential for achieving sustainable healthcare systems and improving public health outcomes. The high benefit-cost ratios, strong returns on investment, and favourable cost-effectiveness of these programs underscore their critical role in reducing healthcare costs and enhancing quality of life. Policymakers and healthcare stakeholders must continue to support and invest in preventive health measures to realise these significant economic and health benefits. The evidence presented in this study reinforces the importance of preventive health strategies in driving economic and public health advancements, advocating for continued investment and policy support to achieve long-term sustainability and improved health outcomes globally.
