
Introduction
Inadequate care during infancy can have lasting repercussions, impacting various sectors and necessitating increased expenditure on health, social, educational, and judicial services. Positive parenting is a growing public health priority and parenting programmes have been shown to be valuable and effective. Universal Early Parenting Programmes are increasingly popular for enhancing positive parenting practices and addressing skill and attitude gaps across diverse populations.
The Efficacy of Universal Parenting Interventions
Research underscores the potential of early parenting programmes in enhancing parental knowledge and skills. While short-term benefits are evident, long-term impacts of universal interventions on parenting and child development are not thoroughly investigated.
Exploring the Parent and Infant Programme
This study looked into the cost and cost-effectiveness of the Parent and Infant (PIN) programme, a universal intervention targeting parental attitudes and responsive parenting strategies during the early years. The researchers piloted the program in two sites in the Republic of Ireland and compared it to services as usual (SAU). They assessed the cost-effectiveness of the program from an Irish health and social care perspective over 24 months. The primary outcome measure was the Parenting Sense of Competence Scale (PSOC), and by focusing on parent satisfaction this analysis sheds light on the programme’s efficacy.
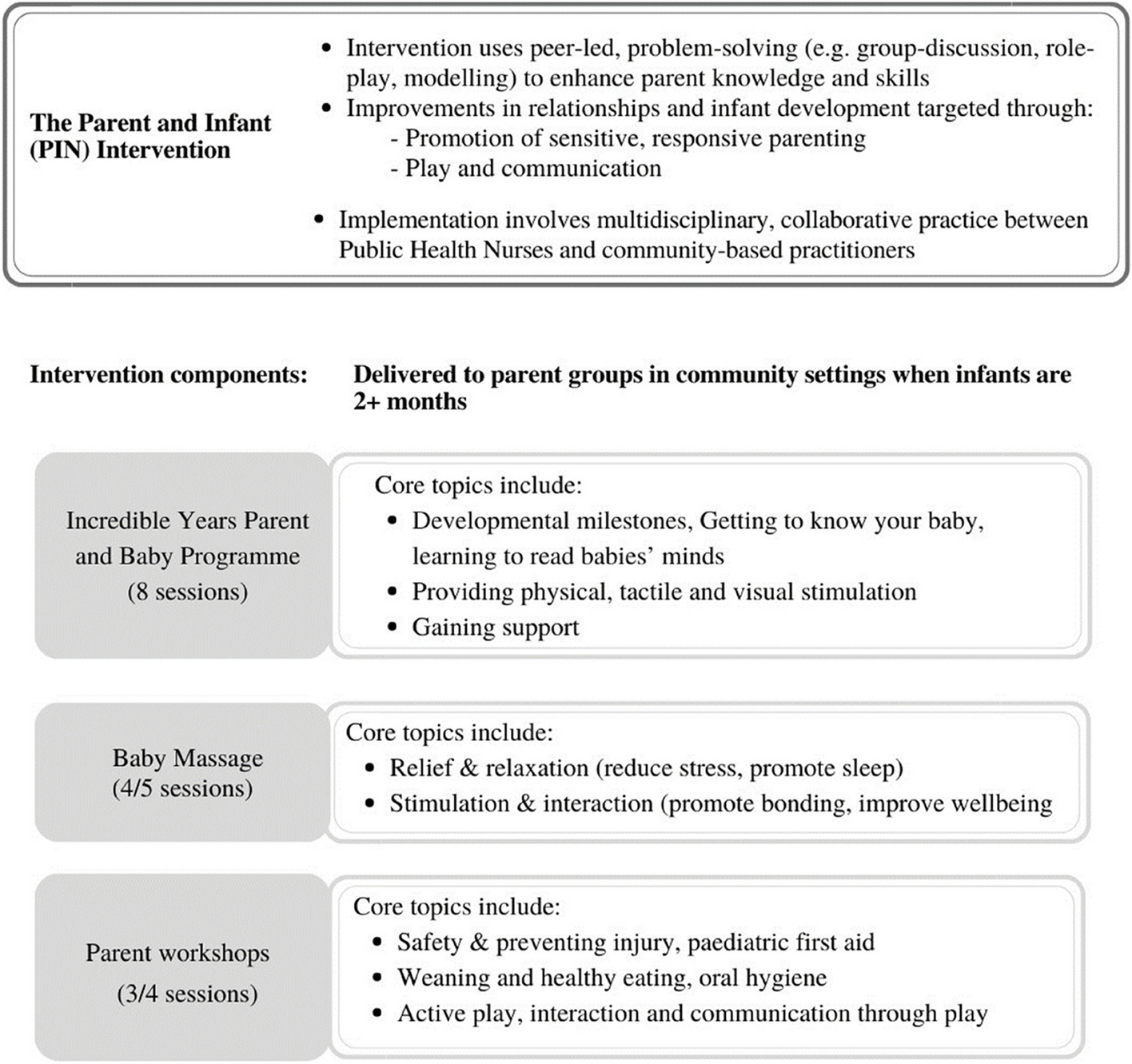
Figure 1. Overview of the PIN programme adapted from Hickey et al., 2020
Results and Cost Analysis
With 163 parent-infant dyads analysed (86 in the programme, 77 control), the PIN programme demonstrated a mean cost of €647 per dyad. The PIN service achieved a mean incremental cost-effectiveness of €614 per PSOC unit gained. At a willingness-to-pay of €1,000 per one unit change in the PSOC, the PIN programme proved cost-effective compared to SAU. The PIN programme showcased positive impacts on parental competence and was viable at a reasonable threshold.
Discussion and Implications
While the study highlights the success of the PIN programme, challenges in evaluating the cost-effectiveness of early interventions persist. The complexities of assessing outcomes in children, coupled with the need for a broader evaluative framework, highlight the necessity for further research and nuanced approaches to appraise the effectiveness of such programmes.
Conclusion
The study emphasise the potential of Universal Early Parenting Programmes in enhancing parental competence and fostering positive childhood behavioural outcomes. Navigating cost-effectiveness challenges, the field requires more research and robust trials to inform policy decisions and resource allocation effectively.
