
Introduction:
The escalating burden of diabetes across the globe is a clarion call for a re-evaluation of medication pricing. With an estimated 537 million people living with diabetes, the financial strain on healthcare systems, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), is profound. Are the prices of diabetes treatments such as insulin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2s), and glucagonlike peptide 1 agonists (GLP1s) justified? What is the cost of production of these products and what are the implications for sustainable diabetes medication pricing?
Access to Insulin: A Dire Need
Insulin remains a lifeline for millions (63 million), yet access is severely constrained. Astonishingly, only half of those requiring insulin have access to it, with the cost being a significant barrier. In the United States, insulin prices are at their peak, whereas countries like China and France have managed to keep prices lower. Notably, using low-cost insulin regimens could slash annual costs to as little as $61, a stark contrast to the $98 to $1300 range for glucose monitoring alone.
New Treatment Options Are Not the Solution
Newer treatment options such as SGLT2s and GLP1s are being recommended as first line treatment for those with additional cardiovascular risk, kidney disease or obesity. But the significant cost attached to these products make them less accessible, especially in LMICs. This would present a large population as approximately 30% of diabetics in LMICs have kidney disease and 27% have coronary artery disease. This analysis showed major cost reductions could be achieved in both these drug classes.
The Monopoly Challenge: Breaking the Oligopoly
The insulin market’s control by three major companies—Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, and Sanofi—has stifled competition and kept prices artificially high. This oligopoly has been a hurdle for new manufacturers, sustaining a market where over 90% of the supply is dominated by these players. The potential for generic and biosimilar products is there, yet patent complexities and business practices have hampered their emergence.
The Promise of Biosimilars: A Path to Affordability
Biosimilars hold promise for reducing medication costs, yet their market entry is costlier than non-biologic medicines. Recent regulatory updates, however, could signal a shift towards more affordable biosimilar options. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and World Health Organization (WHO) have eased requirements for biosimilar insulin, potentially lowering barriers to entry and fostering competition. They would no longer require clinical trials where laboratory analysis and pharma studies have demonstrated high similarities.
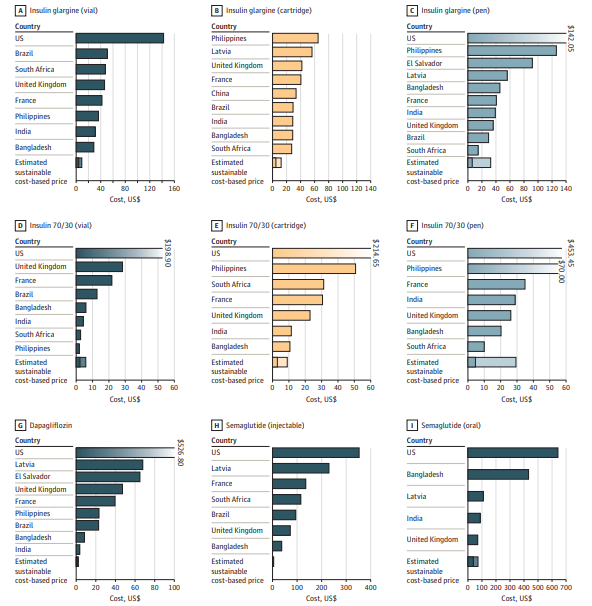
Unveiling the Costs of Manufacture
The economics of manufacturing diabetes medications are not transparent, with pharmaceutical companies typically guarding these figures closely. However, understanding these costs is essential for establishing sustainable pricing models. Some countries will apply a calculation where they produce a maximum price based on the cost of manufacture. For instance, insulin pens can be as low as $1.42 each, which heavily contrasts with the retail prices. This study confirms the price, as the lower bound estimate of $1.20 per pen was observed.
Policy and Pricing: The Road to Equitable Access
The disproportionate burden of diabetes treatment costs in low- and middle-income countries calls for policy interventions. Governments can utilise a range of strategies, from price controls to compulsory licensing, to ensure that life-saving medications are accessible and affordable. Understanding manufacturing costs is critical for informed negotiations and policy-making, setting the standard for sustainable pricing models.
Conclusion:
The analysis indicates a substantial cost reduction possibility with competitive biosimilar manufacture. Human insulin treatment cost might drop to $96 per year, and insulin analogues might decrease to $111. For SGLT2s and GLP1s, the treatment cost per month could fall to $1.30 and $0.75 respectively. This is a perfect time to adopt successful mechanisms from other disease areas. This adoption will ensure affordable and accessible diabetes treatments for everyone.
