
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds great potential in healthcare by enhancing clinical decision-making and patient outcomes. However, a significant gap exists between the development of AI models and their successful integration into clinical practice. Despite the proliferation of AI-based clinical decision support systems (AICDSS), only a meager 2% of these models progress beyond the prototyping stage, leaving the actual clinical impact largely unexplored.
Evaluating Clinical Value through Rigorous Trials
The evaluation of AICDSS through randomised controlled trials (RCTs) stands as a critical step in determining their true clinical value. While some RCTs have been conducted, their outcomes paint a nuanced picture. Although these trials showcase promising statistical performance of AI, nearly half of them fail to demonstrate improved patient outcomes. This discrepancy underscores the complexity of assessing AI solely based on quantitative metrics like accuracy. This may not capture the practical utility of these systems in real-world healthcare settings. Table 1 unpacks the definitions associated with interpreting the patient outcomes. This helps clinicians and researchers shift from the arbitrariness that hinders real-world settings.
| Reported in N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation outcomea | Clinical explanation | Implementation stage | RCTs (N = 64) | Guidelinesb (N = 5) |
| Appropriateness | Is the AI compatible with the clinical workflow and is it useful? | Early | 5 (8) | 0 (0) |
| Acceptability | Is the AI acceptable, agreeable, or satisfactory for the users? | Ongoing | 10 (16) | 0 (0) |
| Feasibility | Can the AI be successfully used as intended by the manufacturer? | Early | 16 (25) | 0 (0) |
| Adoption | Do the users express the initial decision, or action to try or employ the AI? | Ongoing | 6 (9) | 0 (0) |
| Fidelity | Is the AI implemented as intended by the manufacturer? | Ongoing | 31 (48) | 0 (0) |
| Implementation cost | What is the cost impact of implementing the AI system? | Late | 4 (6) | 0 (0) |
| Penetration | Has the AI been adopted by all groups of trained users? | Late | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Sustainability | Is the AI maintained within ongoing clinical operations over time? | Late | 1 (2) | 0 (0) |
Table 1: AI in RCTs, Definitions of implementation outcomes were adapted from the taxonomy of implementation outcomes by Proctor et al (2011).
The Need for a Holistic Evaluation Approach
A comprehensive understanding of AI’s role in clinical practice necessitates a multi-faceted evaluation strategy. Current guidelines like Developmental and Exploratory Clinical Investigations of DEcision support systems driven by Artificial Intelligence (DECIDE-AI) and Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials–Artificial Intelligence (CONSORT-AI), fall short in providing robust measures for assessing AI implementation success. To address this gap, a mixed-methods evaluation approach, proves invaluable in dissecting the various dimensions of AICDSS implementation.
Bridging the Gap in Implementation Evaluation
Despite the increasing focus on RCTs evaluating AICDSS in clinical settings, a gap exists in the comprehensive evaluation of implementation outcomes. While metrics like ‘fidelity’ are commonly reported using quantitative measures, aspects such as ‘acceptability’ and ‘appropriateness’ that demand qualitative scrutiny are often overlooked. This imbalance underscores the need for a more holistic approach towards evaluating the implementation of AICDSS, encompassing factors beyond statistical performance. Figure 1 reiterates the comprehensive value of integrating implementation outcomes in AI in healthcare, revealing an innovative future in the field.
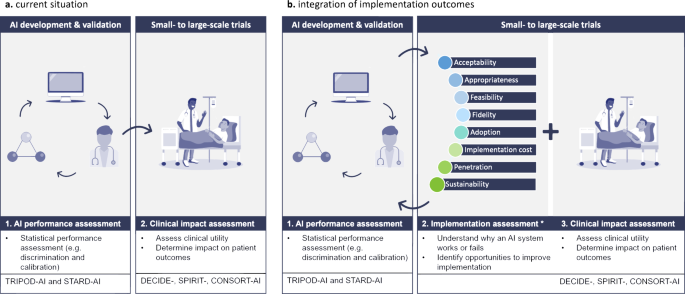
Conclusion
While the efficacy of AICDSS in healthcare settings is crucial, understanding the contextual nuances is imperative. Enhanced systematic reporting of implementation outcomes alongside effectiveness metrics can bridge the existing gap in comprehensively assessing the impact of clinical AI. Embracing an inclusive evaluation framework will not only validate the effectiveness of AICDSS but also shed light on the intricate interplay between AI technology and healthcare delivery.
