Antimicrobial Resistance Costs: A Burden on Healthcare Providers
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and antimicrobial resistance costs are a global challenge with significant implications for healthcare providers. A recent study conducted in two public tertiary hospitals in Ghana, a lower-middle-income setting, quantified the healthcare provider costs (HPCs) due to AMR using both aggregated ingredient costing and step-down costing approaches. The results reveal that AMR patients demand more time and resources from healthcare providers than patients infected with susceptible bacteria or uninfected patients.
The Direct Impact of AMR on Hospitals
The study found that if AMR could be avoided, the extra 5 bed days allocated for treating an estimated 740 AMR patients annually at both hospitals would free up 3700 bed days, allowing for the admission of an additional 451 patients. Moreover, doctors spend an extra 7 hours at Hospital 1 and 3 hours at Hospital 2 caring for each AMR patient admitted to the hospital within a 30-day data collection period.
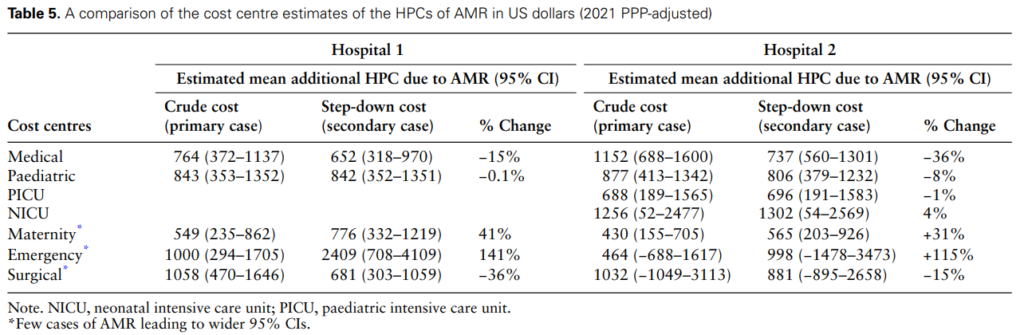
The Cost of AMR
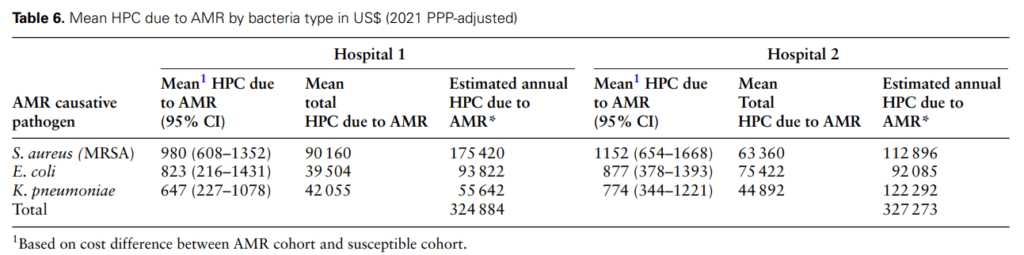
The research also highlighted the variation in costs due to AMR causative pathogens. For instance, treating each patient with MRSA bloodstream infections at Hospital 1 was approximately 33% higher than treating K. pneumoniae and 16% higher than E. coli bloodstream infections resistant to 3GC. The provider cost of treating AMR was highest for the medical emergency unit due to its limited capacity to treat patients with severe and emergency health conditions compared to the general medical unit.
Mitigating AMR: A Matter of Urgency
The findings underscore the urgent need for healthcare providers and policymakers to focus on AMR mitigation measures. Such measures may include general infection prevention and control, effective antibiotic regulation, and adherence to WHO’s access, watch and reserve (AWaRe) recommendation for antibiotic prescription and therapy. The study also advocates for demand-driven strategies, such as point-of-care education regarding antibiotic use and resistance’s health and economic implications, and supply-driven interventions like hospital-wide antibiotic restriction policy implementation.
In conclusion, AMR imposes significant costs on healthcare providers, particularly in lower-middle-income settings. These costs can be avoided through a myriad of infection prevention and control strategies, thus making a strong case for investment in AMR mitigation strategies.
