
Concerning Inappropriate Use of Antibiotics
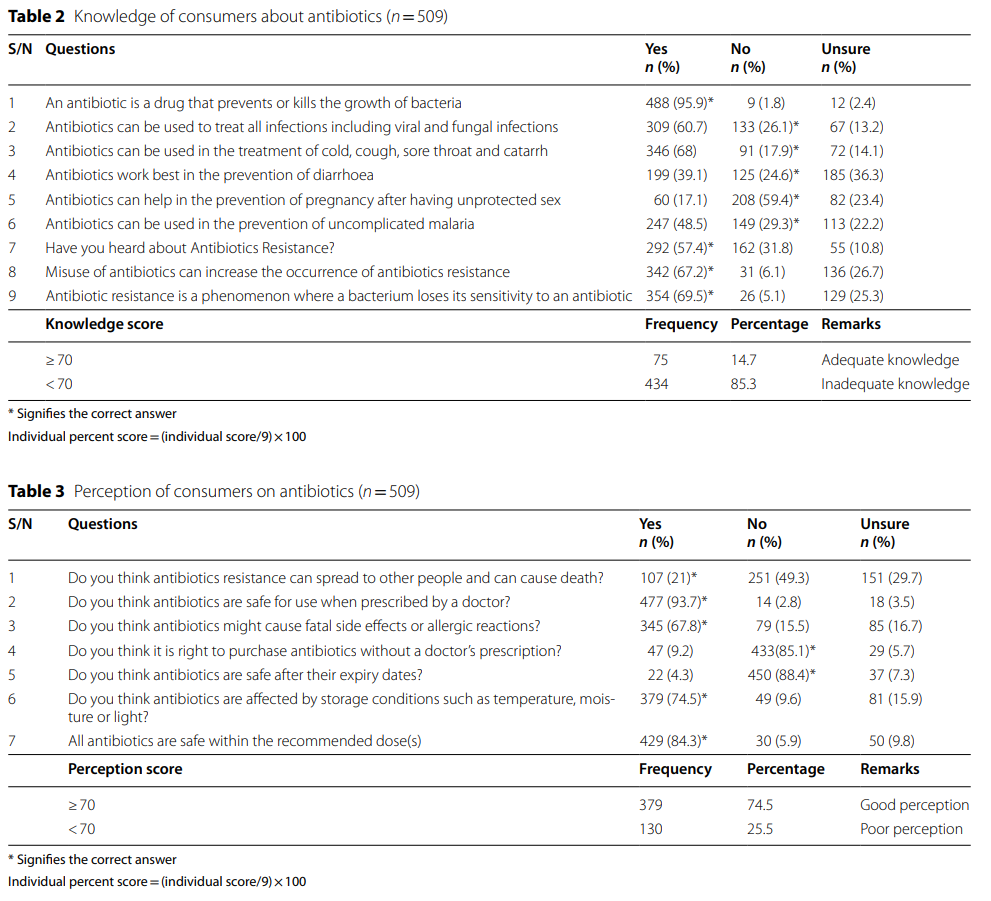
In middle income countries such as Nigeria, the improper use of antibiotics poses a significant risk to the general population’s health. A recent investigation into consumers’ knowledge, perceptions, and the factors related with this usage was carried out in Ibadan, Nigeria. An alarmingly high percentage of consumers (95.9%) felt that antibiotics could prevent the growth of bacteria, and 60.7% believed that they could treat all infections using antibiotics. Unbelievably, 57.4% of respondents were not aware of antibiotic resistance, and just 14.7% of respondents possessed adequate information regarding antibiotics.
Factors That Influence the Improper Use of Antibiotics
The study revealed that 72.5% of customers have used antibiotics within the previous 12 months. Doctors prescribed antibiotics most often for Malaria, with amoxicillin being the most frequently used drug. Several factors significantly influenced the misuse of antibiotics. These included delayed test results, the belief that antibiotics offer instant relief, and the closeness of the pharmacy to a person’s home or workplace.
Findings
This study reveals a crucial need for better public education about proper antibiotic use. Despite respondents having a high level of education, they still lack significant understanding of how to correctly use antibiotics and the risks of misuse. Social influences and antibiotic myths widen this knowledge gap. It’s not only false but also dangerous to believe that antibiotics can cure all diseases, stop diarrhea, or serve as a preventative measure after unprotected sex. These are all myths. Believing these misconceptions can lead to misuse or overuse of antibiotics. This behavior contributes to the global issue of antibiotic resistance.
This study revealed a concerning trend of consumers commonly self-medicating with antibiotics like amoxicillin, ampicillin, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, and metronidazole. The low cost and easy over-the-counter availability of these antibiotics contribute to their overuse. We should avoid this practice because it increases the risk of antibiotic resistance. Another concern is the prescription of antibiotics for non-bacterial illnesses, such as uncomplicated malaria. Protozoa, not bacteria, cause malaria. While many antibiotics can treat malaria, their improper use could create resistant strains of the disease.
Conclusion
The vast majority of customers lacked adequate understanding about the proper way to take antibiotics, which resulted in their inappropriate application of antibiotics. In order to increase understanding and encourage the correct application of antibiotics, specialised educational initiatives are required. There should be a stricter enforcement of the regulations that regulate the dispensing and marketing of antibiotics together with the provision of proper counseling.
